
Cloud technologies are innovative technologies for working on the Internet.Technologydistributed data processing in whichcomputer resources and capacities are provided to the user as an Internet service. If you explain it in an accessible language, then cloud services are your working platform on the Internet, or rather, on a remote server, which is provided as Internet services to realize your goals, tasks, and projects.
Interruptions in the operation of one cloud network server do notwill touch other servers, ensuring an overall smooth operation. In addition, cloud technologies allow you to evenly regulate and pay only for the resources used, without overpayments. For example, cloud cryptocurrency mining services operate on this principle.
The simplest example of a cloud service is— Email. If you work with mail on some service site (gmail.com, yandex.ru, mail.ru) that allows you to use this mail, then this is nothing more than a cloud service that is part of cloud technologies.
Key features of cloud services for the average user:
- Access to personal or corporate information from any computer connected to the Internet.
- You can work with information from different devices (PCs, tablets, phones, etc.).
- No matter which operating system you prefer to work on (Windows, Mac, Linux).
- Different users can view and edit the same information at the same time from different devices.
- If something happens to your device (PC, tablet, phone), then you will not lose important information, since it is no longer stored on the cloud service servers.
- You always use the latest version of programs and do not need to monitor the release of updates.
These are only the most basic features that cloud networks provide, we will describe in more detail all the options for using cloud technologies in this material.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is processing technology.data in which computer resources are provided to the Internet by the user as an online service. The word "cloud" is present here as a metaphor, personifying a complex infrastructure that hides all the technical details.
Definition of cloud computing at first glancevery confusing: it is a model for providing ubiquitous and convenient network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., servers, applications, networks, storage, and services) that can be quickly provisioned and released with minimal management effort and the need for provider interaction.
To better understand what cloud iscomputing, we can give a simple example: previously, to access email, a user resorted to certain software (messengers and programs) installed on his PC, but now he simply goes to the website of the company whose email services he likes, directly through the browser. without the use of intermediaries.
But this example is more suitable for privateclouds We are interested in these technologies in business. Modern implementation began in 2006. Then Amazon introduced its web services infrastructure, which not only provides hosting, but also provides remote computing power to the client.
Cloud Services Classification
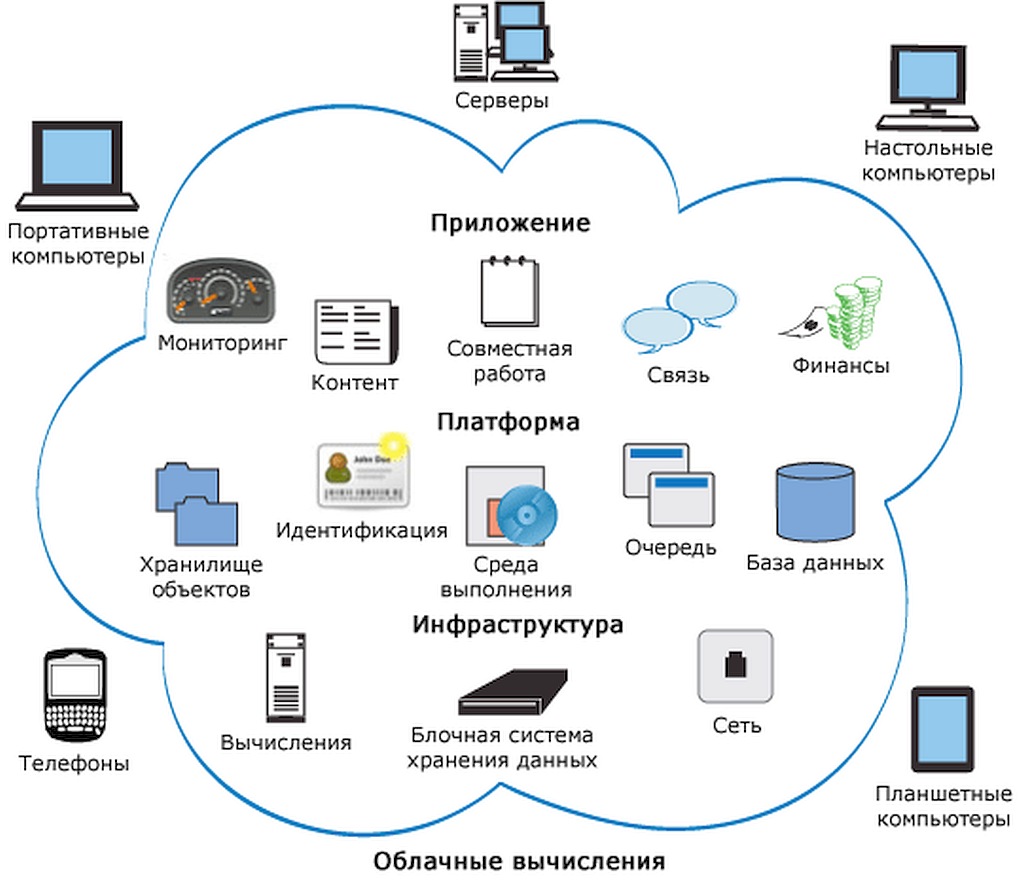
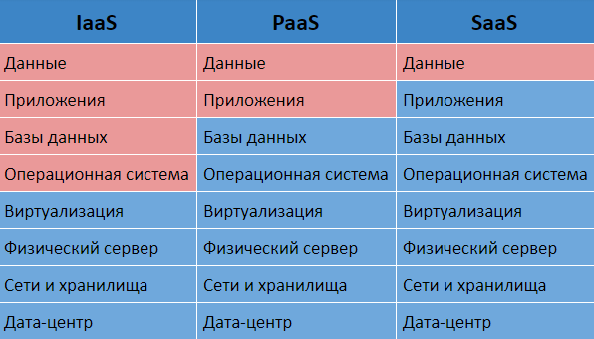
There are three cloud computing service models:
- Software as a Service (SaaS, Software as a Servise).The consumer is provided with software - the provider's applications running on the cloud infrastructure.
- Platform as a service (PaaS, Platform as a Service).The consumer is provided with fundsfor deployment on cloud infrastructure of consumer-created or purchased applications developed using provider-supported tools and programming languages.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS, Infrastructure as a Service).The consumer is provided with processing facilitiesdata, storage, networks and other underlying computing resources on which the consumer can deploy and run arbitrary software, including operating systems and applications.
Data Centers for Data Processing
For storing and handling large quantitiesinformation cloud services use specialized technical solutions, powerful servers, disk storage. Creating and maintaining such technical systems on their own is quite difficult and expensive: maintaining servers requires special technical conditions, separate rooms and qualified personnel. One of the main purposes of data centers is precisely the creation of suitable conditions for the placement of such technical solutions.
Data centers (data centers, data centers - processing centersdata) specialize in the placement of specialized computer devices for storing, processing information, as well as providing communication channels for customers to access the Internet or transfer data.

The purpose of the data center is to ensure guaranteeduptime of the enterprise information system with predetermined levels of availability, reliability, security and manageability. Using technology to create data centers allows you to create backup headquarters for enterprises while maintaining the highest possible functionality of the information system in emergency situations.
The main task of the data center is to createsecure reliable space with favorable climatic conditions for work, guaranteed power supply, thanks to which the tenant company can always get access to its data that is closed to unauthorized users.
Benefits of Cloud Services
Last year, the total volume of the world marketin the field of cloud technologies amounted to about $40 billion. Some experts predict that by 2020 this figure will reach $240 billion. Russia ranks 34th in terms of the introduction of cloud computing into business with an indicator of $250 million.
There are several main advantages associated with the use of cloud technologies:
- Availability.Anyone who has a computer, tablet, or any mobile device connected to the Internet can access information stored on the cloud. The following advantage follows from this.
- Mobility.The user does not have a permanent attachment to one workplace. From anywhere in the world, managers can receive reports, and executives can monitor production.
- Profitability.One of the important advantages is reducedcost. The user does not need to buy expensive computers and software with large computing power, and he is also freed from the need to hire a specialist to maintain local IT technologies.
- Lease.The user receives the required package of services only at the moment when he needs it, and pays, in fact, only for the number of purchased functions.
- Flexibility.All necessary resources are provided automatically by the provider.
- High manufacturability.Large computing power that is placed at the user's disposal, which can be used for storing, analyzing and processing data.
Reliability.Some experts argue that the reliability provided by modern cloud computing is much higher than the reliability of local resources, arguing that few businesses can afford to purchase and maintain a full-fledged data center.
Disadvantages of Cloud Services
- The need for constant connection.To get access to the services of the "cloud" you need a permanent connection to the Internet
- Software and its “customization”.There are restrictions on the software that you candeploy on the "clouds" and provide it to the user. The user has restrictions on the software used and sometimes is not able to configure it for his own purposes.
- Confidentiality.Confidentiality of data stored in public“clouds” currently causes a lot of controversy, but in most cases experts agree that it is not recommended to store the most valuable documents for a company on a public “cloud”, since there is currently no technology that would guarantee 100% confidentiality data
- Safety.The “cloud” itself is enoughreliable system, but upon penetration, an attacker gains access to a huge data storage. Another minus, — This is the use of virtualization systems that use standard OS kernels (for example, Windows) as a hypervisor, which allows the use of viruses and system vulnerabilities
- High cost of equipment.To build your own cloud, you need to allocate significant material resources, which is not beneficial for newly created and small companies
- Further monetization of the resource.It is entirely possible that companies will later decide to charge users for the services provided.
As you can see, there are two sides to the coin. However, this does not harm the development of technology, and maybe even spurs it.
Cloud Deployment Models

Private cloud(English)private cloud) is an infrastructure intended for use by one organization, which includes several consumers (for example, divisions of one organization), possibly also clients and contractors of this organization.
Private cloud may be ownedmanagement and operation of both the organization itself and a third party (or any combination thereof), and it can physically exist both inside and outside the jurisdiction of the owner.
Public cloud(English: public cloud).Infrastructure designed for free use by the general public. May be owned, operated, and operated by commercial, scientific, and government entities (or any combination thereof). Physically exists in the jurisdiction of the owner - service provider.
Hybrid cloud(English)A hybrid cloud is a combination of two or more different cloud infrastructures (private, public or public) that remain unique entities but are linked together by standardized or proprietary data and application technologies.
Public cloud(English)community cloud is a type of infrastructure designed for use by a specific community of consumers from organizations that share common goals (for example, mission, security requirements, policies, and compliance with various requirements).
The public cloud may be incooperative (joint) ownership, management and operation of one or more community organizations or a third party (or any combination thereof), and it may physically exist both inside and outside the jurisdiction of the owner.
Cloud Service Models

Software as a service(SaaS, English)Software-as-a-Service is a model in which the consumer is given the opportunity to use the provider's application software running on a cloud infrastructure and accessible from various client devices or through a thin client, such as a browser (for example, webmail) or an interface programs.
Control and management of the underlying physical andthe virtual infrastructure of the cloud, including the network, servers, operating systems, storage, or even the individual capabilities of the application (with the exception of a limited set of user application configuration settings) is provided by the cloud provider.
Platform as a Service(PaaS, English)Platform-as-a-Service is a model where the consumer is given the opportunity to use a cloud infrastructure to host basic software for subsequent deployment of new or existing applications (in-house, custom-developed or purchased replicated applications).
Such platforms include instrumentaltools for creating, testing and executing application software - database management systems, middleware, programming language execution environments - provided by the cloud provider.
Control and management of the underlying physical andthe virtual infrastructure of the cloud, including the network, servers, operating systems, storage is carried out by the cloud provider, with the exception of developed or installed applications, as well as, if possible, configuration parameters of the environment (platform).
Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS, English)IaaS or Infrastructure-as-a-Service). Provided as the ability to leverage cloud infrastructure to self-manage processing, storage, networking, and other fundamental computing resources. For example, a consumer may install and run arbitrary software, which may include operating systems, platform software, and application software.
The consumer can control the operatingsystems, virtual storage systems and installed applications, as well as limited control over the set of available services (for example, firewall, DNS). Control and management of the main physical and virtual infrastructure of the cloud, including the network, servers, types of operating systems used, and storage systems, is carried out by the cloud provider.
What opportunities do cloud technologies offer for business?
Allow you to get the necessary resources on request, without buying equipment.The cloud makes it possible to flexibly respond to company needs or market conditions.
The company's demand for resources or programs is heterogeneous, for example:
- During sales or seasonal surgesmore capacity to cope with the influx of customers and make sure that the site or application does not fall under load. After the sale, so many resources will not be needed. The cloud allows you to quickly increase the amount of resources used, and then lower it back, so that the service does not fall under load, and you do not overpay for unused resources in decline.
- When you start a company or create a new product, you usually need a minimum of digital resources. If successful, resource requirements will increase; they can easily be received quickly in the cloud.
Since the resources in the cloud are provided bydemand (on demand), you pay only for those capacities that are needed right now. The use of cloud technology allows you to get the infrastructure for digital products, which is easily growing or decreasing depending on your needs.
Allows you to remove part of the load from the IT department. Server deployment and administration is a non-core task for most businesses.
Going to the cloud means that:
- You do not need to buy your own servers, much less build a data center, that is, you reduce capital costs for IT.
- You do not need to hire experts involvedinfrastructure deployment and management: server virtualization, hypervisors, virtual resource allocation, configuration and support of cloud databases and other platforms. This is the responsibility of the provider.
- You can also outsource to the provideradministration of servers, databases, platforms and other services that require highly specialized experts. This is the ultimate level of outsourcing, which is called Managed services.
Allow you to quickly launch new projects or MVPs for startups and research departments.You can rent computing resources fromhelp quickly develop minimally viable products (MVPs) to test business hypotheses. It can be mobile applications and games, machine-learning programs, SaaS solutions that the company sells to customers.
Cloud computing is great for projectswith a high degree of uncertainty, allowing you to quickly start the project, save on equipment and not incur large losses if the hypothesis does not work. And if it works, it's easy to scale the solution.
Allows you to reduce risks in case of failures and accidents.In the cloud, different disaster scenarios are possible.recovery: periodic backups, backup infrastructure and others. Restoring from backups taken at a certain frequency is suitable when maintaining a backup infrastructure is more expensive than keeping services down for some time.
If downtime is unacceptable, companies run incloud backup infrastructure into which data is constantly copied from the main. In this case, the downtime of the services after the failure, if any, is minimal.
What services do cloud networks offer?
Everything related to cloud computing is usually called “aaS”. It simply stands for “as a Service”, that is, “as a service”, or “as a service”.
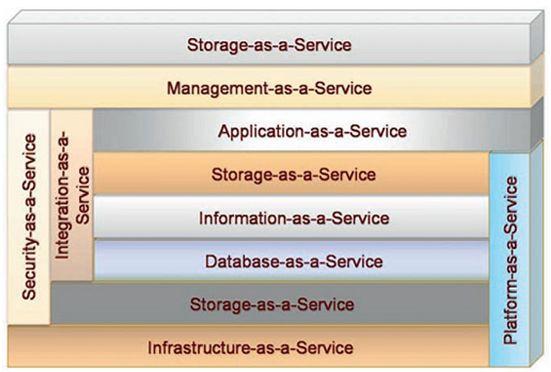
Currently, cloud technologies and, in fact, their concept, involves the provision of the following types of services to its users:
- Storage-as-a-Service
This is perhaps the simplest of the CC services,representing disk space on demand. Each of us has ever encountered a situation where an ominous warning appeared on the monitor: “The logical disk is full, to free up space, remove unnecessary programs or data.” The Storage-as-a-Service service allows you to save data in external storage, in the «cloud». For you, it will look like an additional logical drive or folder. The service is basic for the rest, since it is included in almost all of them. An example would be Google Drive and other similar services. - Database-as-a-Service («database-as-a-service»)
This is probably more for admins, because this thingprovides the ability to work with databases as if the DBMS were installed on a local resource. Moreover, in this case it is much easier to «share» projects between different performers, not to mention how much money can be saved on computer hardware and licenses required for competent use of a DBMS in a large or even medium-sized organization. - Information-as-a-Service («information as a service»)
Makes it possible to remotely use any type of information that can change every minute or even every second. - Process-as-a-Service («process management as a service»)
Represents a remote resource thatcan link together multiple resources (such as services or data contained within a single cloud or other available clouds) to create a single business process. - Application-as-a-Service
Still, maybecalled Software-as-a-Service. It is positioned as “software on demand”, which is deployed on remote servers and each user can access it via the Internet, and all updates and licenses for this software are regulated by the provider of this service. Payment, in this case, is made for the actual use of the latter. Examples include Google Docs, Google Calendar, etc. online programs. - Platform-as-a-Service
The user is provided with a computer platform with an installed operating system and some software. - Integration-as-a-Service
This is an opportunity to receive from the «cloud»a complete integration package, including software interfaces between applications and management of their algorithms. This includes the well-known services and features of enterprise application centralization, optimization and integration (EAI) packages, but delivered as «cloud» service. - Security-as-a-Service («security as a service»)
This type of service provides the opportunityusers quickly deploy products that allow for the secure use of web technologies, email correspondence, and local networks, which allows users of this service to save on deploying and maintaining their own security system. - Management/Governace-as-a-Service («administration and governance as a service»)
Makes it possible to manage and set the operating parameters of one or many «cloud» services. These are mainly parameters such as topology, resource usage, virtualization. - Infrastructure-as-a-Service
The user is provided with a computer infrastructure, usually virtual platforms (computers) connected to a network, which he independently configures for his own purposes. - Testing-as-a-Service
Allows testing of local or«cloud» systems using test software from the «cloud» (no equipment or support at the enterprise is required).
For clarity, we summarize all these services of the “cloud” architecture, in one scheme behind which lies the cloud technologies on which the classification of services is given, by type of service:
A brief history and key stages of technology development
The concept of "cloud computing" originated in 1960, when John McCarthy suggested that someday computer computing would be done using "nationwide utilities."
Cloud computing may seem relativelynew phenomenon. However, their story goes back to the early 1950s, when the advent of mainframes allowed several users to access a central computer.
The first idea of what we call todayCloud computing was voiced by J.C.R. Licklider, in 1970. During these years, he was responsible for creating ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). His idea was that every person on earth would be connected to a network from which he would receive not only data on and programs.
Further, we can distinguish such key stages in the development of cloud technologies:
- Internet bandwidth expansion inThe 90s did not allow us to get a significant leap in development in cloud technology, since almost no technology companies of that time were ready for this. However, the fact of accelerating the Internet gave impetus to the early development of cloud computing.
- One of the most significant events in thisThe area was the appearance of Salesforce.com in 1999. This company was the first company to provide access to its application through the site, in fact this company was the first company to provide its software on the principle of software as a service (SaaS).
- The next step was the development of a cloud web service by Amazon in 2002. This service allows you to store, information and perform calculations.
- In 2006, Amazon launched a service calledElastic Compute cloud (EC2), as a web service that allowed its users to run their own applications. Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3 are the first cloud services available.
- Another milestone in the development of cloud computing occurred after Google created the Google Apps platform for web applications in the business sector.
- A significant role in the development of cloud technologies was played by virtualization technologies, in particular software that allows you to create a virtual infrastructure.
- Hardware development has contributednot so much the rapid growth of cloud technologies, but the availability of this technology for small businesses and individuals. With regard to technological progress, the creation of multi-core processors and increasing the capacity of information storage devices played a significant role in this.
Today, it is safe to say- Modern cloud technologies lead to the expansion of business opportunities. Large investment projects related to the development of cloud computing expect global profits, since the basis of any business is profitability, growing with the use of clouds. They help companies go far ahead, leaving competitors in weak positions. In today's entrepreneurship, the reaction rate to market changes play a particularly important role, so innovative technologies will always be in the top of demand.
Cloud Computing Prospects
IT outsourcing trends will intensify, inincluding computing resources (Infrastructure as a service), storage systems (Storage as a service), data recovery services (Disaster Recovery Service), information security services, subscription software (Software as a service), administration, etc. d.
According to experts, for several yearswe will observe an intensive growth of the cloud services market - at least 25-30% per year, including in remote regions this process will be coupled with the penetration of high-speed Internet. At the same time, the share of cloud technologies in hybrid architectures of information systems of companies will increase, as expertise in the use of clouds, the number of successful business cases and, accordingly, the level of trust will accumulate. Along with the increased use of clouds, the demand for secure private cloud solutions will increase.
In general, clouds will evolve towardsglobal trends, including those from service providers. The services, technologies and SLAs used will be standardized, the government will formulate regulatory documents for the industry, and from a technological point of view, the clouds will become more productive (maximum computational speed when processing a huge amount of information) and less costly.
There is another side to the development of cloudtechnologies: exponential growth of data - the bulk of the stored information will fall on archive copies that will not be in demand and will not be deleted.
As for the long term, thenthe development of cloud services will be coupled with the introduction of machine learning systems: artificial intelligence, neural networks, augmented reality, as well as neural interfaces, quantum teleportation, etc.
Already in deep developmentthe concept of fog computing, which involves using for storage and analysis of data not the central nodes of the network of data centers, but the resources of a large number of geographically distributed personal devices (PCs, tablets, gadgets, drones, household appliances, etc.), in fact, implementing The principle of distributing computing power to almost all devices around us.
Share this material on social networks and leave your opinion in the comments below.
</p> 5
/
5
(
1
voice
)





