More and more people are learning about Bitcoin, and at the same time, less and less attention is being paid to the technology behind it.basis.We have written more than once about blockchain technology and everything related to it. But today let's try to break down its characteristics, purpose, varieties according to the points. And in general - let's just talk about what the blockchain really is.
</p>Part 1. Important characteristics of the blockchain - basic information
Getting acquainted with blockchain technology, you immediately hear about the mind-blowing growth of cryptocurrencies, but first, it is worth understanding the key characteristics of the blockchain in order to gain basic knowledge.
This article will just help you gain such knowledge. There will be no technical analysis here, but instead blockchain technology will be looked at in a comprehensive manner.

illustrations: Medium
So, in the first part, we will focus on the important characteristics of the blockchain. There are five of them:
- Transparency.
- Truth and Trust
- Security
- Efficiency
- Quality and precision
1. Transparency
Following the release of Socialdilemma ”interest in data collection and privacy has increased significantly. We live in a world of opaque data. Data about our lives is collected around the clock, seven days a week. Where we shop, where we eat, where we go, where we meet with friends, where we work. All this data and many more are collected by companies, some of which we know nothing about.
However, the use of blockchain technology will make data collection transparent. Anyone with access(everyone has access to the public blockchain, but the private one needs authorization), will be able to see what data is stored, what it is used for and through whose hands it passed.
The basic principle is shared, open data.The reason why the data is being collected is known to the entire network. To ensure that the data is being collected properly, it is possible to check the details on the blockchain, which are transparent to everyone with access.
Transparency is a significant advantageblockchain. We live in an age when we want to “own” our data. We want our relationship with large corporations to no longer be one-sided. Controlling your data is critical as more and more data is created about us - data is created with every action we take, and companies use it to their advantage. This may continue, but companies need to be transparent about what data they store about us and how that data is used.
Data transparency made possible byblockchain has increased the traceability of data generated by the interactions of businesses with consumers, but it is important to also transfer this to the relationship between businesses. Companies in different industries violate human rights by hiding behind opaque supply chains. Blockchain implementation will force these companies to correct their behavior.
2. Truth and Trust
The fundamental property of the blockchain isimmutability of data. In essence, when data is entered into the blockchain and verified, it remains there forever and cannot be changed or destroyed. This is combined with the decentralized nature of the blockchain, where all nodes have the same copies of the data. This means that there is a single view of truth.
In the world of post-truth and fake news, blockchaintakes on the role of a hopeful guardian of truth, helping to resolve problems with trusted parties. Since transactions on the blockchain are transparent and immutable, all events are permanently recorded in history.
However, it should be remembered that the technologyblockchain is still new and relies on its device and inputs. Blockchain will not solve the problem of errors and poor quality inputs. The data entered into the blockchain may be incorrect, but if all nodes agree that this is true, then they will be added and cannot be removed. However, incorrect data and its source can be relatively easy to find.
"Beliefs are a more dangerous enemy of truth than lies" - Friedrich Nietzsche
3. Security
The data added to the blockchain is immutable andhave a time stamp. This is a fundamental requirement for any blockchain and is critical to its success. The ability to ensure that there is one true data that cannot be deleted and changed gives our data world more transparency and solidity.
The data is protected using cryptography.It is a key part of the blockchain that ensures that data is only used for agreed-upon purposes and therefore is protected from theft and attacks.
4. Efficiency
One of the more common advantages of blockchainall they say is the elimination of intermediaries. True, we are not necessarily talking about their complete elimination, since they may still be required to one degree or another. However, we mean a significant reduction in their role and their transformation into a useful element of the ecosystem. The technology will eliminate the need for those intermediaries that add to the time and cost of processes. This will contribute to better management and efficiency of the entire ecosystem.
Partial or complete elimination of intermediaries depends on the device of a particular blockchain. The key to success is consensus and the carefully thought out mechanisms associated with it.
In addition, efficiency is increased thanks touse of smart contracts. These are contracts that are programmed in the blockchain and are activated under certain conditions. Smart contracts automate certain transactions on the blockchain according to specified conditions or principles. In the simplest case they have the form"If X happens, then execute Y"... Low-level bulk transaction automation is critical to the efficiency of blockchain technology.
5. Quality and precision
Data can be entered into the blockchain from anysource, for example manually, from IoT devices, from another database, or via an API. All this data is validated before being added to the blockchain. This improves their quality. In addition, if the data is entered from a secure database or secured IoT device, then it will also have higher accuracy and quality.
But, as already mentioned, there is a possibilityadding incorrect or bad data to the blockchain. However, the technology makes it possible to quickly find and track bad data, which helps solve the problem of bad data much faster than with previous database technologies.
Conclusion
This was just the most basic explanation of the keycharacteristics of the blockchain, but it provides an insight into this incredibly complex topic. You will learn more about all this in the following parts. To begin with, it is important to get a foundation on which to build your knowledge.
Part 2. Blockchain - Equity Formula?
After reviewing the first part of the keycharacteristics of the blockchain, we can understand the reasons for such a great interest in decentralization and information exchange. But this is not just a hype in the online community. This is discussed by governments, academia and business. The idea of a world where everyone is equal and everyone has a fair share can become a reality thanks to blockchain technology. While this is a very idealistic vision of the future, Anthony Welfer summarized the world we live in now beautifully:
“We all now understand that we were born and livein a centralized world. We get centralized identity cards, visit centralized educational institutions, then work for centralized organizations, where we get our number. "
After reading this quote, it is easy to admit that welived like this for hundreds of years, so the transition to a decentralized system cannot be quick. You also need to understand that most people do not want to change. They are satisfied with the status quo, since that is all they know. And threatening what they know can scare people because they think their lives will change radically.
Recognizing that we are centralized and most people don't want to change,is a decentralized world possible?It is impossible to say what will happen in the future or whether some event will change human thinking towards a more decentralized ideology, but now people are not ready for change.
However, there is no reason to lose hope and interest.When you examine the real-world use cases for blockchain and the idea of true decentralization, it becomes clear that blockchain is not only a technology, but also a belief system focused on an equal and just world. Blockchain will not come to the fore in the near future, but by combining it with other new technologies, we can be less dependent on centralized organizations and authorities and understand that these authorities control and do not control.
Bitcoin Phenomenon
However, to see the changes, you do not need towait for the future. Just look at the explosive growth of bitcoin, and it becomes obvious that the idea of decentralization is now attracting a lot of media attention. And even many governments are trying to enter the crypto space, after in 2017 they disowned anyone who showed support for it.
In 2018, when Bitcoin was falling in value, many speculated that the authorities were trying to manipulate the free crypto market in order to cause a crash and bankrupt miners. Was it true?
If you look at fully regulated markets,governed by regulatory structures, which makes them centralized, and then to the unregulated world of cryptocurrencies, you can see that the latter have much more freedom to avoid manipulation(note that this is just an assumption about how open decentralized markets are to manipulation, not a statement about how it really was).
I am by no means claiming that cryptocurrencies- the best use of blockchain because I don't think so, but this is by far the most popular use case for blockchain technology and the sector is still relatively small compared to what it might be. Even at its current small scale, this technology gives enough concern to the authorities to oppose it and its truths.
Conclusion
As technology becomesmore mature and more and more applications will appear, the control structures will continue to make noise and interfere with its development. My only hope is that they will intervene in a reasonable and honest way and not through manipulation of the network and the market. In my opinion, centralized organizations now see decentralization as a threat, since there are no obvious business models that would be consistent with this technology, and therefore there are no clear paths to profit. But as more businesses are deployed and more use cases are implemented, business development options will be fully explored and business models developed.
Yes, I am convinced that blockchain is a formulafairness, but most are looking at the beautiful surface of technology and not exploring the systemic shifts that must occur for us to live in a decentralized and just world.
“There are no beautiful surfaces without awful depths” - Friedrich Nietzsche
Part 3. Public, private and hybrid blockchain networks
There are many different types of distributed ledger technologies (DLTs), many of which are classified as blockchain. We will focus on three main ones and discuss their differences:
- Public.
- Private.
- Hybrid.
Different types of blockchain networks play different roles andperform different tasks. Most believe we need a hybrid world where blockchain networks interact with each other. In recent years, we have seen the emergence of many blockchains and DLTs, and they all need to work together for the unique aspects of each network to contribute to a larger ecosystem.
Public networks
The public blockchain network is 100% open and notrequires permissions to access. Anyone can join and access. Anyone can conduct transactions on the network and view them in the ledger, but only if the rest of the network considers these transactions to be valid.
In addition, the data of the unit and the identity of the person,conducting the transaction will remain anonymous. The most popular example of a public blockchain is Bitcoin. At the highest level, Bitcoin is an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof. The consensus mechanism used in Bitcoin is called proof of work. The main idea behind Bitcoin is to provide a medium of exchange without the need for a central structure to mediate transactions.
Private networks
On a private network, on the other hand, usersmust obtain permissions or access rights to use the network, view the registry, and add data Such networks also control who can be the validator of transaction blocks and limit the range of those who can participate in the network's consensus mechanism.
An example of a private network is Hyperledger Fabric.Hyperledger is a cross-industry solution that seeks to provide a range of plug-and-play components to help enterprises scale. Since it is a private network, its creators have much more control over who can join it and who can view it.
Hybrid networks
The hybrid network essentially combines aspects of the public and private blockchain.
Typically, a hybrid network consists of two components, which can be summarized as a publicly accessible blockchain and a closed network(available by invitation only)... Hybrid networks ensure that all transactionswill be confidential but can be verified on an immutable public blockchain. Everyone who joins the hybrid network has equal rights to view and add transactions, and user identities remain anonymous.
An example of a hybrid network is Interledger, a platform for communication between ledgers.
This part turned out to be very short, but it summarizes the main types of blockchain networks that can be found now.
Part 4. Blockchain and international trade

: Unsplash
So, in the first three parts we looked atquite extensive topics related to the blockchain. Now that we have a foundation in place, we can delve deeper into the discussion of blockchain and what it takes for the technology to scale.
In this part, we will focus on internationaltrade. Many believe that if a solution can be found to integrate blockchain into international trade, then it will be much easier to solve problems in other areas.
To delve deeper into this topic, you needconsider many different aspects, such as current problems and proposed solutions, as well as how blockchain can be implemented to solve some of these problems, and what is needed for this.
Current issues
There are many problems in international trade now, fromunavailability of certain markets and regions prior to managing the flow of customs documentation and data. The emergence of technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things has served as a catalyst for innovation to remove some of the barriers to trade on a scale never seen before. In this new wave of innovation, companies have also begun to actively implement blockchain. An example is IBM and its TradeLens platform, which aims to digitize supply chains using blockchain technology.
With this in mind, it is important for businesses to develop a flexible, open strategy for future international trade that will actively use blockchain and other technological solutions.
The first major international trade issue we will focus on istransaction costs associated with intermediaries and paperwork... As everyone knows, international transactionshighly dependent on intermediaries and work with documents. Goods in supply chains are inspected, processed and authorized by many different authorities and companies. Since they are located in different countries with their own rules, this increases the cost of time, resources and money, which, in turn, burdens those who wish to produce goods and have access to different markets.
There are many types of international tradedocuments that are issued and processed throughout the supply chain, but for the purposes of this article, we will consider an example of a bill of lading - a document issued by a carrier as confirmation of receipt of goods for transportation. The bill of lading requires extensive coordination between different organizations and operators with associated administrative costs and time. Consequently, all this paperwork is vulnerable to errors or deliberate misrepresentation, which can damage the reputation of organizations and entail additional costs and wasted time.
Reduction of bureaucratic obstacles totrade is one of the main tasks to be solved. Technology can reduce unnecessary interactions that lead to duplicate documents and administrative paperwork.
The second problem we will consider isinformation exchange... Currently in supply chainsthere are constant streams of limited and inconsistent information. This is so common that it regularly creates barriers to trade. With the frequent exchange of information between all parties, problems inevitably arise with the quality of data, errors or their late arrival. Data is not always fully available to those who need it. And this leads to additional delays and duplication, due to which goods may not reach their final destination on time, which increases the costs of producers.
Unimpeded exchange of information betweensupply chain actors, as well as customs officials and regulators, will improve confidence in the origin of goods and the accountability of businesses. This brings us to the third and final issue that we will consider -expanding the use of preferential trade access... Each country has a set of tradeinstruments that improve preferential market access for domestic producers and broaden consumer choices. One of the most influential instruments is the free trade agreement (FTA), but there is growing concern about the underutilization of trade preferences guaranteed by the FTA. The conditions for greater two-way market access can be very challenging.
For example, a textile manufacturer from country Amay be subject to a duty when exporting a certain product to country B. An FTA may help reduce or eliminate this duty. In most cases, in order to benefit from this exemption, an exporter from country A must demonstrate compliance with the rules of origin of the country to which it is exporting. To do this, you need to prove that the product really comes from where it is claimed from. Usually, exporters are in no hurry to make all documents and certificates of origin of goods, as this can cost more than the duty they would pay without preferential access. This example demonstrates the serious problems of this process. First, it is difficult to understand the rules for obtaining preferences. Secondly, in order to take advantage of the preferences, you need to go through cumbersome procedures for obtaining documents. The use of technology can reduce or eliminate complex disincentives designed for businesses to gain access guaranteed by the FTA.
Current solutions
Having considered the current problems of internationaltrade, we can move on to the technological solutions that are currently in use. As you know, with the advent of the Internet, businesses were able to develop and invest in new directions. Advances in technology have reduced the natural obstacles created by distance and simplified the complex web of rules and regulations.
But when we focus on internationaltrading, it is important to note several specific advances that have been implemented. The introduction of data analytics, tracking technologies, IoT devices, RFID technologies and artificial intelligence are widely known. These technologies are able to identify the past and current location of goods in the supply chain in order to reduce the costs of manufacturers for a detailed audit (of course, only in theory - you can write an entire article about the disadvantages of this process).
In addition, the United Nations Facilitation CenterTrade and Electronic Business (UN / CEFACT) has developed guidelines for the implementation of electronic information flows to simplify and standardize procedures. Finally, one of the most notable advances is the one-stop shop. These systems are used by customs organizations, allowing businesses to electronically submit applications for certificates, licenses, permits and customs declarations, which reduces the number of channels of interaction with various officials, regulators and inspectors to one and, as a result, significantly reduces the paperwork and inefficiencies associated with with duplication.
Changes through blockchain integration
Many people understand that the integration of blockchain into international trade will solve many problems, but the question is:is blockchain capable of completely revolutionizing international trade... First of all, it should be understood that the blockchain is notpanacea. Its key properties, such as immutability, proof of origin and verification, can certainly change international trade, but it is not the only technology that can do it. Blockchain will be just one of many new technologies that will transform international commerce. Blockchain integration will reduce transaction costs by eliminating the need for paperwork and administrative hurdles created by third parties.
One of the main advantages that blockchainwill bring international trade, is the optimization of documentation. A huge amount of paperwork is now required, and given the intense nature of international trade, this means documents suffer from errors, losses and, in some cases, fraud. Blockchain integration can reduce paperwork and manual checks. However, this does not mean that blockchain is the only solution. It is still far from the complete digitalization of international trade processes, since some kind of paperwork is still required. However, blockchain optimization can facilitate more transactions in supply chains, which will expand international trade. For example, by participating in a blockchain network, customs organizations will be able to more accurately and in a timely manner collect the data necessary for the passage of goods through the supply chain. Information about location, buyer, seller, etc. will be recorded on the blockchain instead of paper documents.
Interesting read: Scott Nelson on global supply chain transformation at the Internet of Agreements conference
Digital ledgers also allow all parties totransactions simultaneously see the same information about the status of the cargo. This facilitates communication between the parties and, in essence, provides mutual trust.
Another area where blockchain can improveinternational trade is international data flows. A blockchain-based network can provide trust between different platforms by integrating disparate data from different sources. Additionally, blockchain can enhance the security of data flows, preventing document fraud and counterfeit goods in international supply chains. Verification at different stages of supply chains can be a big advantage. Blockchain automatically records data after it is verified and stores it in chronological order without changing previous records(however, in some cases there is a problem of incompatibility with the GDPR - this will be discussed in one of the following parts).
How it works?
So that the blockchain can be used ininternational trade, there are many aspects to consider. It is important to consider regulation because technology and technical interoperability are not enough to eliminate paperwork. Completely seamless trading requires a legal framework that recognizes digitized documents and transactions.
Although there is a lot of investment in technology right now,It is worth noting that the situation with the legislative recognition of such instruments as electronic signatures and documents is such that we are still far from the international trading system, where paper can be dispensed with. By replacing traditional workflow with standardized smart contracts, paperless and automated trading can be achieved, but smart contracts do not currently fall under the definition of legally binding contracts. Nonetheless, policymakers should seize this opportunity and consider how regulation can be made more flexible in order to favor the development of such technologies. Since one of the benefits of blockchain is the ability to integrate data from different sources, it is important for regulators to build mechanisms that recognize and favor this opportunity.
If you look at international standards, then onThere has been little progress on this front yet, but that can be expected to change as Bitcoin is on fire again in 2021 and more blockchain startups are popping up than ever. The contribution of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which is currently developing 11 international standards for blockchain, ranging from terminology to taxonomy and ontology, governance regulations, privacy and personal information protection, may be important.
Finally, it is also important to reach an understanding.Various stakeholders in business, civil society and governments should develop a common understanding of blockchain and its implications for international trade. The involvement of all parties is the key to introducing blockchain into international trade.
Blockchain can have a huge impact onthe international trading system through solutions that promote trust, security, transparency and consumer confidence. And it should be a race for innovation, not regulation.
Part 5. Blockchain Consensus for Beginners

In this part, which will be long enough,we will look at what consensus is in general and what types of consensus mechanisms are used now in the blockchain space. If you're looking for a complete beginner blockchain consensus review, then you've come to the right place. Stock up on tea and cookies - and let's go!
When studying blockchain, it is important to understand howverification. And it is based on a consensus mechanism. In the blockchain, the transaction is verified WHEN it is added to the ledger, whereas in the traditional database, the transaction is verified AFTER it is added.
The task of the Byzantine generals
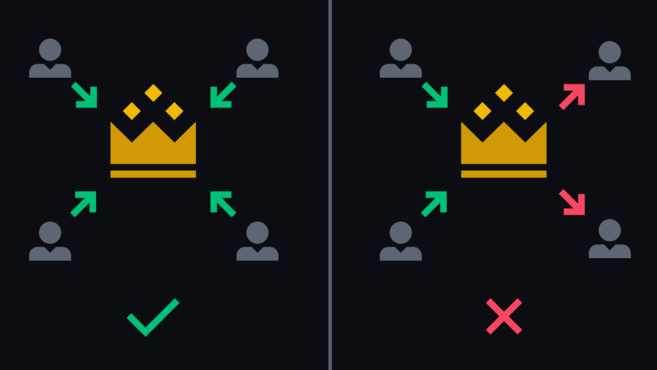
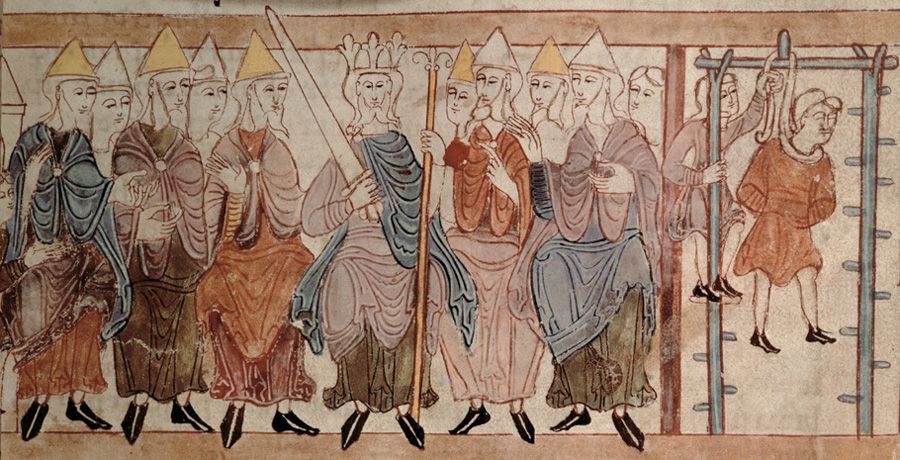
All generals will succeed with a simultaneous attack (left). If some retreat while others attack, then they will be defeated (right). : binance.com
To begin with, we should be transported to the EastThe Roman Empire to consider the task of the Byzantine generals. This is a logical challenge, originally formulated in 1982. It illustrates how a group of generals can have communication problems when trying to agree on the next step. We need to imagine that each general has his own army and they are all located in different places around the besieged city. The generals must agree on whether they will attack or retreat. The final decision doesn't matter; the main thing is that they all agree with him. Thus, the following criteria should be considered:
- Each general must make a decision and vote to advance or retreat.
- Once a vote has been cast, it cannot be changed.
- All generals must come to a common decision and put it into action in a coordinated manner.
However, they can only communicate through messengers, andthe main difficulty is that messages can be delayed, lost, or destroyed. And even if the message is successfully delivered, one or more generals may, for one reason or another, decide to send a false message in order to mislead others, leading to complete failure.
If we apply this task to the blockchain, thengenerals are the nodes that must come to a consensus on the current state of the system. This means that most of the participants in the distributed network must agree and perform the same actions in order to avoid disruptions. The ability of a system to withstand disruptions arising from the task of Byzantine generals is called Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT). In other words, the BFT system is able to operate smoothly when some nodes do not transmit information or act in bad faith.
There are many ways to build a BFT blockchain depending on the consensus algorithm. The consensus algorithm is the mechanism by which the blockchain network reaches consensus.
What is consensus and why is it needed?
The dictionary defines consensus asagreement by all parties involved in a transaction or process that something is true.
The blockchain ecosystem has developed many differentalgorithms that allow the parties to reach such an agreement that certain data are valid. The purpose of these algorithms is to provide reliability in a network where there are many unreliable participants. Below we will look at the most popular consensus mechanisms.
Proof of work (PoW)

illustrations: BitNews
In short, in this case the minerscompete with each other in solving a complex computational problem. While this is difficult to solve, the correct solution is easy to test. When a miner has found a solution to a problem, he can broadcast his block of the network, where then all miners will check if the solution is really correct.
As an example, Bitcoin is a blockchain system,which is supported by the collective work of many decentralized nodes. Some of these nodes are known as miners and are responsible for adding new blocks to the blockchain. To do this, miners must pick up a pseudo-random number known as a nonce. This number, when added to the block data and passed through a hash function, should yield a result that satisfies certain conditions. For example, the hash must start with four zeros. When a suitable result is found, other nodes will check it and the miner will receive a reward. Therefore, it is impossible to add a new block to the blockchain without first finding a valid nonce, which gives the desired block hash. Each confirmed block contains a hash that represents the work done by the miner. Therefore, this is called Proof of Work (PoW).
Proof of ownership (PoS)

Proof of ownership (Proof ofStake, PoS) was introduced in 2011 on the Bitcointalk forum to address PoW issues. While both algorithms aim to achieve consensus on the blockchain, they accomplish this in different ways.
PoS algorithm uses pseudo-randomselecting a node that will be the validator of the next block. The selection is based on the amount of cryptocurrency the node holds. For example, a node that holds 1% of the network's wealth can only create 1% of PoS blocks. It is worth noting that in PoS, the process of creating blocks is not called mining, as in PoW, but forging. PoS cryptocurrencies often start by selling pre-mined coins or launch with PoW and then move to PoS.
In PoW systems, miners are rewarded inthe form of a newly created cryptocurrency. In PoS systems, transaction fees are rewarded. Users wishing to participate in forging must reserve a certain amount online. The size of this collateral determines the probability of a node to be selected as a validator that will create the next block. The higher the deposit, the more chances.
You probably think that the network will favorthe richest nodes. To solve this problem, there are several methods that are added to the selection process. The two most popular methods are randomized selection and coin age selection.
The randomized selection looks for nodes with the combination of the lowest hash and the highest collateral. Since the amount of the collateral is public, other nodes can usually guess the next validator.
In the second method, the nodes are selected based onhow long their tokens were pledged. The age of coins is calculated by multiplying the number of days the coins were held as collateral by the number of coins in the collateral.
When a node created a block, the age of its coinsis zeroed, and it must wait a certain amount of time before being able to create a block again. Thanks to this, nodes with large collateral cannot dominate the blockchain.
It is important to know that each blockchain using PoS has its own set of rules, which its creators consider to be the best combination for themselves and their users.
With regard to security, the bail serves tothe validator is financially motivated not to create or confirm fraudulent transactions. If the network detects such a transaction, the corresponding node will lose part of its collateral and the right to be a validator in the future.
Delegated Proof of Ownership (DPoS)
Delegated proof of ownership(Delegated Proof of Stake, DPoS) relies on groups of trusted network users to confirm transactions between everyone else. The network votes for such delegates based on their reputation and trust in the community.
DPoS was developed in 2014.American crypto businessman Daniel Larimer. Many consider such a process, where coin holders vote for delegates responsible for confirming new blocks, as a more efficient and democratic version of the PoS algorithm.
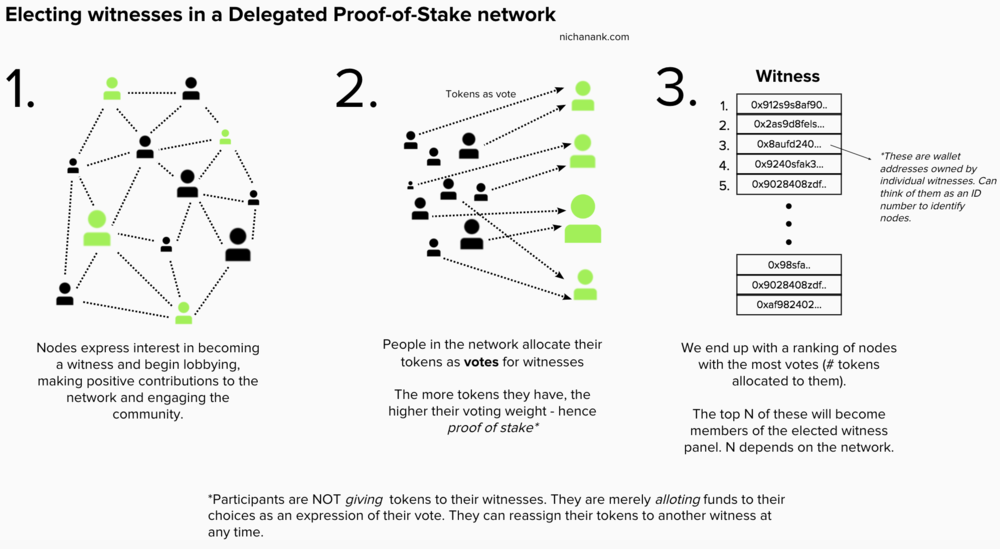
DPoS was conceived as a digital implementationdemocracy. Depending on the consensus rules of the DPoS network, from 21 to 101 delegates are elected by voting. These delegates, also known as "witnesses", confirm transactions and are rewarded for adding blocks to the blockchain. Each network member has a number of votes proportional to the number of coins he owns, or he can delegate his votes to another member.
DPoS can have different implementations.Compared to PoW, DPoS is a more productive and energy efficient solution. This algorithm also contributes to decentralization, since anyone can become a delegate and large mining farms are not needed to validate blocks.
Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)

: Investopedia
Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)developed at the beginning of 2016by Intel, and therefore requires a special CPU and instruction set called Software Guard Extension (SGX) to operate. SGX allows applications on a machine to execute code that is considered trusted in a secure execution environment. In PoET, the trusted code determines the timeout.
PoET is an alternative consensus mechanism,whose work is completely different from those discussed above. Netizens must use a secure software environment that allows them to prove that they are expecting a truly random amount of time. The user who waits the least time verifies the block and adds it to the registry.
PoET is often used in private and hybridnetworks. Each node on the network must wait a random amount of time before it is declared the winner and can add a new block to the register. There are two very important factors in the operation of a PoET network:
- The nodes of the network choose their latency fairly at random and do not increase their chances by deliberately choosing a short time.
- The node with the shortest latency (the winner) should indeed wait the corresponding amount of time.
The advantage of PoET is that the workflowresembles a PoW system, but without high energy consumption. Instead of intensively using resources, the node processor can be idle for a certain time or switch to other tasks, which improves efficiency.
Proof of Importance (PoI)
Proof of Importance (PoI)– a consensus mechanism using importancenodes in the network to determine who will confirm new blocks. The importance of a node is determined by various criteria, which collectively show its effectiveness.
The PoI consensus mechanism is used in the NEM cryptocurrency(New Economy Movement). The process of adding new blocks to the blockchaincalled harvesting here. Nodes with higher importance than others have a higher chance of being chosen to add a new block to the blockchain. The first criterion to meet before becoming a harvester is to hold at least 10,000 coins.
PoI takes into account general support andthe importance of each node. To calculate the importance, graph theory is used, with the help of which the importance of nodes in the system is determined. This requires three variables:
- Reserved balance.
- Partners in transactions.
- The number and volume of transactions in the last 30 days.
What is the reserve balance?
- A network node must have at least 10,000 reserved coins to be able to become a harvester.
- The more coins a user has, the higher his PoI rating.
- A node must keep these reserved coins in its account for X days before they can affect its rating.
As can be seen from the considered consensusmechanisms, in recent years in different blockchains - both public and private and hybrid - different methods of information verification have been actively developed. Hopefully, you have gained some basic knowledge on this topic.
Part 6. Impact of blockchain on personal data management

: Medium
In this part we will talk about account management.data. This is an important topic for our future, which has many interpretations. As you read further, you will notice that blockchain-based credential management focuses on personal identification, but would also like to touch on the identification of assets and goods.
So let's figure out what management iscredentials, sometimes also called identity and access management. Identity management includes all the processes and technologies in an organization that are used to identify and authenticate someone to gain access to the services of that organization or others.(such organizations may include government agencies and medical institutions).
Currently, credentials are highly dependentfrom papers, as in the case of a birth certificate, which may lie somewhere in your basement, and a copy of it in the city administration. Therefore, they are highly vulnerable to loss, theft and fraud. The implementation of digital credentials significantly reduces painful bureaucracy, significantly increases processing speed and provides better interoperability between different services and organizations. But if your digital credentials are stored on a centralized server, they become a target for hackers. Since 2017 alone, hackers have stolen over 600 million personal data, such as addresses and credit card numbers. This is because most digital credential management systems are weak and outdated.
Our credentials must be portable andverifiable anywhere, anytime, and this is possible thanks to digitization. But it's not enough that the data is just digital. They must also be kept confidential and secure. Let's look at examples of some of the problems:
- Governments– lack of interoperability between different government structures, which leads to excessive bureaucracy, which increases processing time and costs.
- Businesses– current requirements for storing customer dataand employees are a source of great responsibility for companies. Identity theft can result in huge fines due to GDPR violations or decrease customer trust in the company, damaging its reputation.
How can these problems be solved?
Cryptography in Credential Management
When we need to prove anything related toby our personality - even by name or age - there is always an authentication process taking place. The verifier confirms that the data we provide about ourselves is correct. This is usually done by checking our ID.
In connection with these account verification processesdata concerns about confidentiality. Should the verifier that asks me to verify my name with a passport or driver's license have access to the rest of this document? Should the person asking me to prove my age also know more information about me?
An authentication method known asZero-knowledge proof, thanks to the use of cryptography, allows one person to prove to another that he knows certain information or meets certain requirements, without the need to directly disclose the information on which this proof is based. The person who checks the evidence does not know anything about the information on which it is based, but is convinced of its validity. This is especially useful when the person providing the evidence does not trust the person performing the verification.
Hence, credential management withusing blockchain allows a person to prove that his personal data meets the requirements without disclosing this data. Zero knowledge proof is best demonstrated in Andrew Yao's Millionaire Problem.
Blockchain-based credential management solutions
Distributed ledger technologies enable everyonenetwork participants have the same source of truth, where the validity of the data can be verified without disclosing it. This can be directly applied to credential management.
When it comes to managing credentials on the blockchain, there are three parties involved: owners, issuers, and credentials verifiers.
Account ownerdata stores its data in an electronic wallet in order to be able to use it to prove statements about itself to a third party (verifier).
Credential issuer– a trusted party such as a localgovernment, which issues credentials to their owner (user). By issuing credentials, the issuer certifies their validity. The usefulness and reliability of the data depends entirely on the reputation of the issuer.
Thanks to blockchain, verifiers do not needcheck the validity of the data itself in the provided proof, or you can check in the blockchain itself the validity of the identity and the certifying party (such as the government), on the basis of which it is possible to determine whether to confirm the proof.
Confirmation of evidence is based on the verifier's judgment about the reliability of the certifying party (issuer).
What exactly happens on the blockchain when using a credential management system?
In short, only links andappropriate certification of verified user credentials. This confidentiality is ensured by the non-correlation principles underlying pseudonymization.
For verification purposes, the registry stores the following:
- Public decentralized identifiers (public DIDs) and corresponding DID descriptor objects (DDOs) with verification keys and endpoints.DID – unique identifiers for verificationdigital personal data that is controlled by the owners of that data. DIDs are independent of centralized registries, authorities, or credential issuers.
- Scheme– formal description of the structure of credentials.
- Credential definitions– descriptions of the various proofs of identity or qualifications issued by the authorities, such as a passport, which are kept in the registry.
- Cancellation registers– the opportunity for issuers to withdraw their applications. The cancellation register communicates cancellation information published by the issuer to the rest of the world.
- Evidence of consent to provide data allows you to prove consent to provide data or receive it.
How can blockchain fraud and theft of credentials be prevented?
When managing credentials usingblockchain, each user will most likely keep their digital data in a wallet on some device like a phone, so this begs the question:what if he loses his phone or gets stolen?
In such cases, there are two main steps.The first is to revoke the device's authorization to use credentials. Digital credentials are only valid when used on an authorized device. If a user's phone is lost or stolen, they can use another authorized device, such as a PC, to record on the blockchain that the phone's authorization is being revoked. This is the modern equivalent of canceling a lost credit card. Such a blockchain entry will take effect immediately and will not allow anyone to use the credentials on such a device.
Deauthorizing a device prevents the thief orto the one who found the phone, impersonate the user in order to enter into a new relationship. The second step prevents that person from gaining access to existing relationships between the device and other people or organizations. This is to revoke key pairings from existing relationships.
Impact on Assets - Business Perspective

It is important for retailers to have some kind of accountdata, as this may be critical for the sale of age-restricted products such as alcohol, but it also simplifies the offering of services and other benefits. With verified credentials, the retailer can make personalized offers or provide loans and financial products.
Each person has an identity card– this is a necessity, but it will also be valuable if assets and devices also have their own unique and verified credentials. One of the biggest challenges in retail today is online and offline tracking. It is much more difficult to find out the client's preferences when he is offline, but with verified credentials(and permissions granted by their owner)retailers can personalize their offerings to the specific customer using the device, solving the complexity of omnichannel shopping.
This method has previously been studied by largesocial media platforms through tracking user data and then selling that data to advertisers. Many were dissatisfied with the fact that companies make money from personal data. When used to manage blockchain credentials, the consumer will have full control over who has access to their data, with the ability to revoke permissions. If a consumer does not want the company to store their data, they will revoke their data from that company.
Human perspective is the future
As we have seen, thanks to the use ofblockchain technology can securely manage credentials. This can be applied to simple tasks such as proof of age, addresses, etc. While this is a great start, there are many more possibilities where you can use blockchain so that everyone in the world has their own credentials. There are billions of people in the world today without any personal documents. This means that they do not have access to a bank or, for example, a doctor. They also cannot travel and rent or buy housing.
The real value of the blockchain is the ability to createand protect the economic credentials of billions of people living in extreme poverty. This not only allows for better digital credentials, but also creates an opportunity for sovereign identity.
Facebook has previously tried to fix this problem,creating a stablecoin called Libra. But this project has failed as Facebook has lost public confidence in recent years. Libra's idea was to provide everyone in the world with access to financial services. It was assumed that funds could be sent using text messages and that this currency would be provided by a number of companies from different industries. Behind Libra is a promising concept that allows new technologies to increase the number of people who have access to financial services, and therefore create digital credentials for them.
There is much more to write about the application on this topic.Internet of Things and supply chain applications. But it is important to gain a basic understanding of blockchain-based credential management as this topic is gaining in importance.
Part 7. How to Overcome Barriers to Blockchain Implementation

: Medium
Implementation of any technological innovationsmeets challenges, and blockchain is no exception. But the key is to make sure the benefits outweigh the risks. In this part, we will look at some of the potential problems.
People don't like change
People tend to get attached to what they havealready there, even if they don't like it, and don't welcome changes. Change is often associated with fear and unhappiness, meaning that most people are afraid of what they don't understand. It should be clear from the previous parts that blockchain will not be a quick and easy solution to all problems, but nothing really worthwhile happens overnight.
In case of any changes, there are always those whowants to be among the pioneers in new technologies. Such people are very important to the community and organizations should help them develop blockchain technology.
Unfortunately, in the blockchain space there are a lot offake news related to cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, due to which people do not see all the benefits of blockchain technology. But the situation is gradually changing, as more and more use cases appear and more and more influential organizations are introducing blockchain and cryptocurrencies into their businesses. It is important to note that blockchain is not Bitcoin. Bitcoin is just the first use of blockchain, and as more use cases emerge, the less blockchain will be misunderstood.
It is necessary that people understand that the waystoring data on the blockchain is completely different from what is now considered the norm. For many people, this is a big change. They are used to entering data and then validating and confirming it after the transaction. As we already know, everything happens differently in the blockchain: the data is checked and confirmed when it is added to the ledger. It will take time before people get used to such changes.
Scale and complexity
When viewed from the perspective of industries and organizations processing thousands or millions of transactions per day, the issue of scale and complexity is acute.
How to unite hundreds, thousands or hundreds of thousands of participants? How to reach consensus? What if the consensus mechanism fails?
These are all important questions asked by companies.like IBM, and they need to be answered in the process of implementing blockchain solutions. When implementing blockchain, a lot depends not so much on the technology itself as on people and processes. Companies can solve the scaling problem by bringing in people with the right expertise to integrate and leveraging the entire ecosystem.
Standardization
Any technology has a period when it is not yetStandardization has formed and competing startups are desperately trying to become the only standard in the industry. Now there is such a race to become the “main” blockchain solution, which is meaningless, since the main idea is to create an interconnected ecosystem of different blockchains interacting with each other(after all, how to achieve a single standard in a decentralized environment?).
Nevertheless, it is necessary to agree on a set of standards for the entire blockchain ecosystem, similar to what can be seen in the telecommunications industry.
The next stage of standardization isinteroperability and the existence of robust processes and standards for system interoperability and data reconciliation. This will allow different blockchain solutions to interact with each other, creating a cohesive ecosystem.
Whatever standards are adopted, it is important thatthey were understood and applied to the entire ecosystem. They need to cover all geography and all use cases, so their development will be a long process.
User acceptance
For the growth of blockchain technology, it is important to payattention to user acceptance. If users cannot interact with the blockchain solution in a simple and intuitive way, then they will not use it. It is important for developers to understand that the end user should be able to use this technology as easily as other technologies today. If it is even a little more difficult, users will abandon it.
For user acceptance of technologyblockchain education is critical. Users need to be educated about the benefits of using blockchain technology. The better the education, the more users will embrace the technology and start developing new use cases.
Younger generation
This last point is perhaps the most important.As you know, the younger generation does not agree with the current system does not trust the government, law enforcement agencies and large organizations that govern the world. It wants transparency, reliability, better understanding and the ability to influence the future of the world.
Since I myself belong to the younger generation, II see people accepting the ideology behind this technology. Blockchain is put on a par with other new technologies, which is important, but it is seen through rose-colored glasses as an ideological solution, and not as a complex problem. It is necessary for people to focus more on the practical elements of the blockchain, on its real use cases, and not just talk about what opportunities it carries for the future.
This technology will be built on small projects,included in the ecosystem, and not on any one technology company offering a single solution. The focus should be on gradual, step-by-step problem solving, rather than trying to overthrow the government overnight.
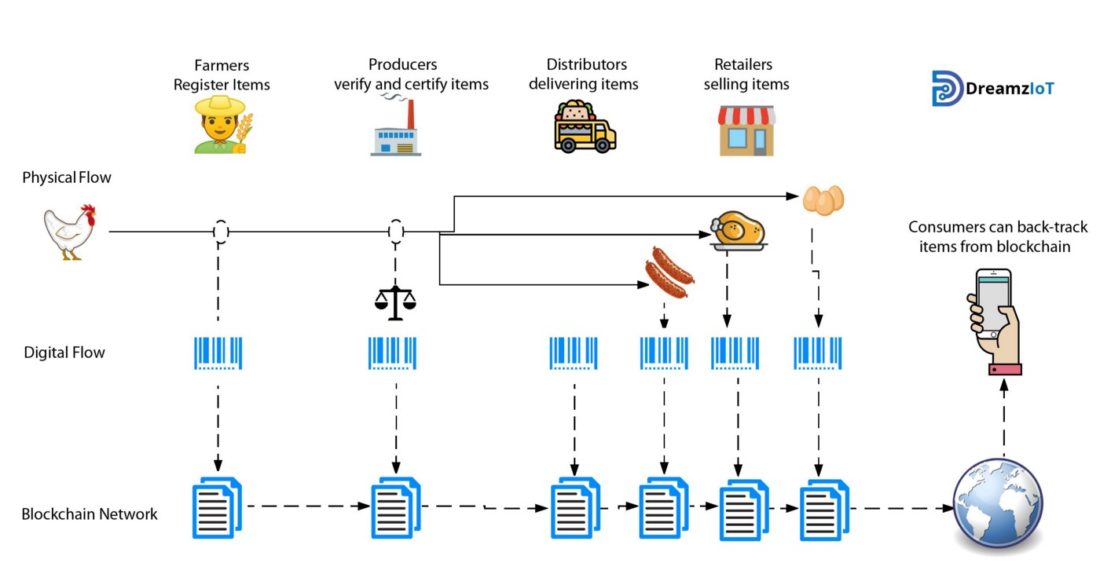
Part 8. Tracking goods using the blockchain

The ability to accurately trace an item and its components is one of the top use cases for organizations. The transparency and robustness of blockchain technology makes it easy to track goods.
The use of blockchain technology for tracking goods has several advantages:
- Better traceability of supply chains to ensure compliance with corporate standards.
- Less losses due to counterfeits and the gray market.
- Better transparency and consistency in contract manufacturing.
- Reduced paperwork and administrative costs.
- Transparency of the entire supply chain - from raw materials to final goods.
- Deeper comparison of suppliers, leading to a more efficient supply chain and better prices.
- Better predictability of goods receipt.
: Medium
For example, blockchain can be very useful in food supply chains, where the ability to trace all stages from raw materials to the final product sold to consumers is very important.
There are many product tracking solutions in today's complex supply chains, but they mostly cover only certain parts of the supply chain.
Most supply chains have the ability to track one step back and forth. This means that I can tell who I received the goods from and to whom I handed them over.
In complex supply chains of goods such asfood or medicine or other regulated products, traceability is especially important. These supply chains require complete transparency of all ingredients and the conditions in which they are stored.
Blockchain technology can simplify chainssupply and provide regulators with access to data stored throughout the chain. If you add to this the use of QR and RFID-enabled IoT devices, you can accurately track what is happening with goods such as medicines and their current status. The benefits of better traceability are evident in the case of a product recall. Today, it takes an average large global retailer about five days to track the entire supply chain and spot a problem, and blockchain integration will reduce that time to minutes.
Part 9. Can blockchain coexist with GDPR?

: Medium
How Blockchain and Shared Can CoexistData Protection Regulation (GDPR)? What needs to be changed here for blockchain to have a future? In this part we will explore where we are now and what solutions are proposed.
The General Data Protection Regulation gives citizenscontrol over who can collect their personal data and what happens to them. That is why you are asked to consent to the processing of data when you visit the site.
Companies around the world are now strivingcomply with the new regulations, because otherwise they will be penalized. How does this relate to blockchain? First of all, you should study a little about GDPR terminology. The European Union calls the companies that store your data “data controllers” and those who work with your data, analyzing it, “data processors”. In most cases, the controller is also the data processor, but these can be different companies (this is important). It is the data controller who must comply with the GDPR.
Another important point is that the GDPR only applies to the personal data of EU citizens. All companies holding any personal information of EU citizens must comply with the regulation.
What is meant by personal data?The law states that this is "any information associated with an identified or identifiable natural person." While this seems straightforward as most people think their personal information is name, age, and gender, it also includes your phone number, credit card number, and even IP address. The same goes for the address of your Bitcoin wallet, since this string of letters and numbers can, albeit indirectly, be associated with a specific person.
So, having found out what personal data is,data controller and data processor, you can consider how this conflicts with the blockchain. There are three problematic articles in the GDPR: Article 16 on the right to data clarification, Article 17 on the right to be forgotten and Article 18 on the right to restrict data processing.
Article 16 - data clarification
Article 16 gives you the right to rectification of data onyou that someone else has. You can change existing data or add new ones if you think that the current data is inaccurate or incomplete. Adding data to the blockchain is not a problem, but changing previously added data is contrary to blockchain principles.
Article 17 - right to be forgotten
The same applies to article 17 on the right to be forgotten.The inability to delete data from the blockchain means that you cannot exercise this right. Consequently, blockchains cannot comply with the GDPR and store data of EU citizens.
Article 18 - restriction of processing
Finally, Article 18 gives you the right to prohibitcompanies to perform certain actions with your data. This can be done if the data is inaccurate or has been collected illegally. The problem here is that most blockchains are completely open source, which allows anyone to get a copy of all data and do whatever they want with it, which means you have no control over who processes your data.
Is there any hope?
The first solution is to encrypt the data beforeaddition to the blockchain, but this is now a gray area in the legislation. Using strong encryption techniques such as elliptic curves means that only the person or company with the decryption keys can do anything with the data. To then delete the data, it is enough to destroy the keys, so that the encrypted data becomes useless.
Another solution is to store personal data notin the public, but in the closed blockchain. Since in such a blockchain access is controlled and limited by a few known trusted parties, data management will be easier. This will comply with Article 18 of the GDPR, but the closed blockchain is still immutable, so Articles 16 and 17 will not be complied with.
The last solution is zero proofdisclosure. It is a technology that allows you to prove that something is true without revealing the data itself. In the case of cryptocurrency, it is possible to prove that the transaction took place without revealing how much money was transferred or to whom (this is used in Zcash). Zero knowledge proofs are GDPR compliant as the data will be stored but not disclosed.
Current state of affairs
In September 2020The European Commission, in its publication on questions and answers on digital finance, noted that it is closely monitoring to ensure that consumers can control their data. The Commission also stressed that compliance with data protection regulations, in particular the GDPR, is a prerequisite for a data-driven financial sector.
Further explaining that crypto assets are a digital representation of rights to funds that can be sent and stored electronically using certain technology(known as distributed ledger technology)The Commission emphasizes that such assets are inextricably linked to blockchains, as they are contained in the blocks that blockchains are composed of.
Pilot proposals from the European Commission with regard tomarket infrastructure for cryptoasset transactions is an essential step. It is important that the commission also notes weaknesses in the legislation and intends to propose appropriate amendments where current legislation presents clear problems for the application of distributed ledger technology in the market infrastructure.
Ideally, these pilot proposals should clarify conceptual difficulties as long as there is no established law enforcement practice.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is difficult at presentbring it in line with the GDPR, but this is definitely not impossible. There are promising prospects in this area and a breakthrough is planned with the adoption of new standards and laws, so there is no reason for pessimism.
Part 10. Impact of blockchain on international shipping

illustrations: BitNews
International cargo transportation is an extensive topic,covering many different components, such as the regulation of international trade, which we have already discussed in the fourth part. Therefore, here we will consider this topic only in the most general terms, and if you want to learn more, you can conduct your own research.
International cargo transportation
Currently, the freight marketis a vast ecosystem with a large number of participants - from container owners to ports and customs agents - and a lot of paperwork.
For each container shipped from oneport and arriving at another, about 50 paper documents are required. It is a very inefficient system with frequent delays and errors, not to mention lack of transparency and limited scheduling capabilities.
International cargo transportation is one of the mostrecognized blockchain applications, however this is not an easy task. Many companies are focusing on specific parts of this large-scale process, which makes significant improvements in these sectors possible. It will take years for an ecosystem of solutions to develop for the entire process, but the involvement of a large number of stakeholders ensures that real progress is constantly occurring.
For example, IBM's TradeLens platform aims to digitize the entire Maersk supply chain using blockchain.
Some benefits and consequences
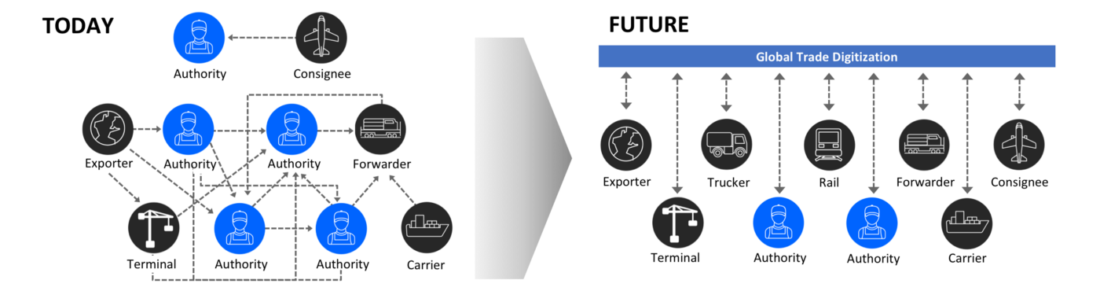
An illustration from IBM: how cargo transportation works now, and how everything will happen in the future
It cannot be denied that the world is internationaltrucking is huge and incredibly important, and blockchain technology can improve current legacy systems in many ways. From the aforementioned fact of 50 documents for each container, the potential of the blockchain to eliminate all this paperwork is already evident.
For the blockchain revolution to take place, hundredstransport lines and thousands of interconnected businesses around the world - including manufacturers, banks, insurers, brokers and many others - must develop a protocol that allows all new systems to be integrated into one large-scale platform. This has already begun and continuous progress is expected.
Blockchain will significantly improve predictabilityreceipt of goods, which will allow all parties involved to prepare in a timely manner, having all the information about the cargo and its location on the ship, which will significantly reduce the time in the port.
Thanks to significantly improved transparency and accuracy of deliveries, it will be possible to know when the goods will arrive at the port and when they will be unloaded so that transport can be sent for them at the right time.
In 2014the world economic forum estimated that processing trade documents costs 1/5 of the cost of transporting goods. Removing administrative barriers in supply chains can improve international trade more than eliminating duties. And the benefits won't be limited to transportation. Improving communications and border administration with blockchain can generate an additional $ 1 trillion in international trade per year.
In conclusion
So, we have considered 10 aspects for whichor otherwise capable of affecting the blockchain. Perhaps these are not all the directions and potential changes that this revolutionary technology has prepared for us, but so far the events are seen as follows.
</p>