Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin is not backed by anything. He is provided with the sameany kind of money: the reliability of their monetary properties. Money is not a collective hallucination and not just a belief system. Throughout history, different means have become money, and each time it was not a coincidence. Goods that become money have unique properties that distinguish them from other market products.
</p>More details can be found in the book “Briefthe history of money ”, but among the unique properties of monetary goods that make them especially useful as a medium of exchange are rarity, durability, divisibility, interchangeability and portability. For each new variety of money, the characteristics are improved, making the pre-existing forms obsolete, and every time when some product becomes money, some other ceases to be money. In fact, the comparative advantages of one money surpass the advantages of another, and Bitcoin is no exception. It represents technological advancement in global monetary competition. It surpasses gold and fiat money systems, based on the monetary properties of gold.
Bitcoin is better than its predecessors in cashproperties. Bitcoin is of finite rarity and is easier to share and easier to move than competitors. It is also more decentralized and, as a result, more resistant to censorship and distortion. Only 21 million bitcoins will be created, and each bitcoin is divided up to eight decimal places (up to one hundred millionth). Funds can be transferred to anyone and anywhere in the world without the need to obtain permission, and the final calculations do not rely on third parties. In general, in terms of its monetary properties, it is far superior to any other types of money used today. And these properties are not random and do not exist in a vacuum. Improved monetary properties of Bitcoin are provided and supported by a combination of cryptography, decentralized nodes that control the implementation of a common set of consensus rules, and a stable network of miners that guarantee the integrity and immutability of the transaction registry. Currency itself is the cornerstone linking the system together, creating economic incentives that enable the pillars of security to function. Nevertheless, the monetary properties of Bitcoin are not absolute; they are valued by the market in comparison with the properties of other monetary systems.

: Shutterstock
Every time dollars are exchanged forbitcoins, the number of dollars and bitcoins in the world does not change. Only the relative preference of a particular currency changes. When the value of bitcoin rises, this means that market participants are increasingly choosing to hold bitcoins instead of dollars. The higher dollar price of bitcoin means you need to sell more dollars in order to purchase the appropriate amount of bitcoins. So the market evaluates the relative strength of monetary properties. Monetary properties - input, price - output. When evaluating the monetary properties of Bitcoin, a natural question arises: whose monetary properties are more reliable - Bitcoin or the dollar? What is the dollar (or euro, yen, etc.) provided with? When trying to answer this question, they most often refer to the fact that the dollar is provided by the government, army or taxes. However, the dollar is not provided with any of this. Neither the government, nor the army, nor taxes. Governments tax what is valuable, but the product is not valuable because it is taxed. In the same way, armies defend what is valuable, and not vice versa. And the government cannot dictate the value of its currency; it can only dictate its proposal.
Venezuela, Argentina and Turkey havegovernment, army and tax authorities, but their currencies have depreciated significantly over the past 5 years. Although this is insufficient evidence, the example of each of these states contradicts the idea that the value of a currency depends on the government. Episodes of hyperinflation should be sufficient evidence of flaws in fiat money systems, but, unfortunately, they are not considered as such. Instead of understanding hyperinflation as the logical outcome of all fiat systems, most simply see it as evidence of improper monetary management. Such a simplified view neglects the fundamental principles, as well as the dynamics that guarantee monetary depreciation in fiat systems. Although the dollar is structurally more stable as a global reserve currency, the functional basis of all fiat money is the same. The dollar is simply the strongest among the weak. If you better understand the mechanisms that support the dollar (and all fiat systems), you can get a basis for evaluating the mechanisms that provide bitcoin.
Why does the dollar have value?
The value of the dollar did not arise in the free market. It originated as partially representing gold (and originally also silver). In effect, the dollar was the solution to the characteristic limitations of convertibility and mobility of gold. Initially, it depended not on its own properties, but on the monetary properties of the metals on which it was based. Also, from the very beginning, the system was based on trust: accept dollars and trust that they can be converted into gold in the future at a fixed rate. The dollar system is based on restrictions and, therefore, the insolvency of gold as money, and without gold, the dollar in its current form would not exist. Here is a brief overview of the history of the relationship between the dollar and gold:
| 1900 | The Gold Standard Act of 1900 defined gold as the only metal into which the dollar was converted. The dollar was converted into gold at $ 20.67 / ounce. |
| 1913 | In accordance with the Federal Reserve Act of 1913, the Federal Reserve System (FRS) was created. |
| 1933 | President Roosevelt, by Executive Order 6102, banned gold savings, requiring citizens to exchange gold for dollars at $20.67/ounce under penalty of a fine of up to $10,000 and/or 5-10 years in prison. |
| 1934 | President Roosevelt signed into the Gold Reserve Act, devaluing the dollar by about 40% to $ 35 an ounce of gold. |
| 1944 | The Bretton Woods Agreement formalizedthe ability of foreign governments and central banks to convert gold to dollars (and vice versa) at $ 35 / ounce and set a fixed exchange rate between the dollar and other currencies. |
| 1971 | President Nixon officially put an end to the convertibility of the dollar into gold, effectively eliminating the Bretton Woods system. The value of the dollar has changed to $ 38 / ounce of gold. |
| 1973 | The US government has changed the price of gold to $ 42 per ounce. |
| 1976 | In 1976, the US government finally untied the value of the dollar from gold. |
Over the course of the 20th century, the dollar evolved from a currencybacked by reserves into a currency backed by debt. While many people constantly wonder why the dollar has value after the end of the golden era, the most common explanation is still that it is either a collective hallucination(i.e., the dollar has value simply because we all believe in it)or it’s connected with the government, the army andtaxes. None of these explanations is based on the fundamental principles and is not a fundamental reason why the dollar saves value. Today, the dollar retains value due to debt and the relative rarity of dollars compared to dollar-denominated debt. In the dollar world, it all depends on the credit system. Nominal GDP, in essence, depends on the size and growth of the credit system, and taxes are a derivative of nominal GDP. Government financing mechanisms (taxes and budget deficits) depend on the credit system, and it is the credit system that allows the dollar to function in its current form.
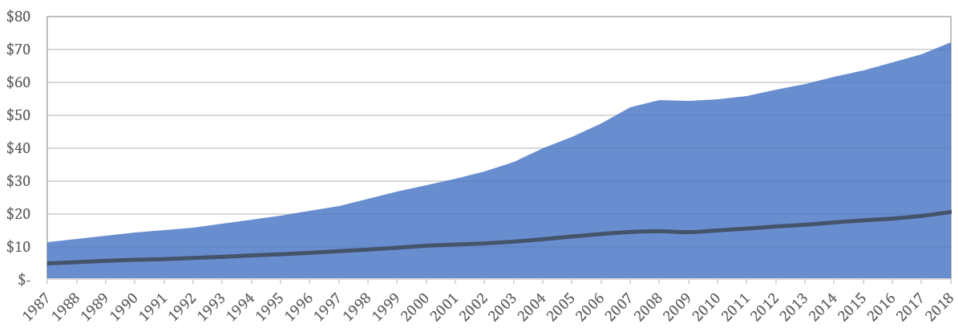
Ratio graphUS public debt(entire credit system, shaded area)
AndNominal GDP(in trillions of dollars, dark line)
: Unchained capital
The size of the credit system several timesexceed nominal GDP. Since the credit system is also several orders of magnitude larger than the monetary base, economic activity is largely coordinated by the distribution and growth of credit. However, over the past three decades, credit growth has far outpaced GDP growth. Credit expansion drives the nominal runway, which ultimately dictates the nominal level of tax revenue.
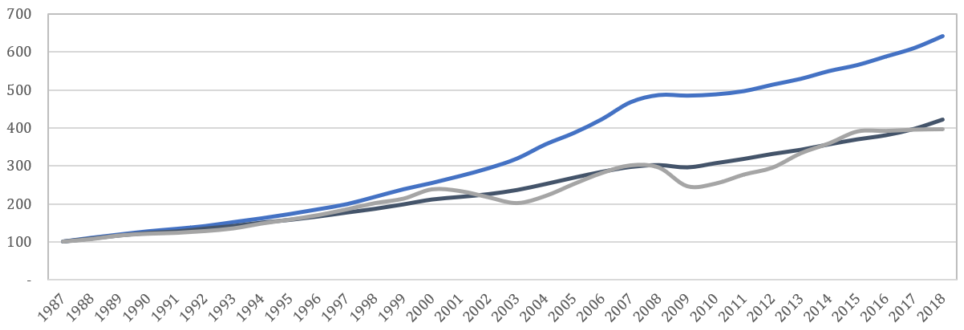
Ratio graphUS public debt(whole credit system, blue)
Nominal GDPand (purple)
Tax revenue(gray), in trillions of dollars.
: Unchained capital
According to the Fed (report Z.1), today in the US credit system $ 73 trillion of debt, but in the banking system only 1.6 trillion real dollars. That is how the Fed controls the relative stability of the dollar. Debt creates future demand for dollars. For every real dollar, there is about $ 40 of debt. If you take a dollar loan today, you will need to purchase dollars in the future in order to repay it, and now every dollar in the banking system is loaned 40 times. The ratio of the size of the credit system to the number of real dollars gives the dollar a relative rarity and stability. In short, everyone needs dollars to pay off dollar loans.
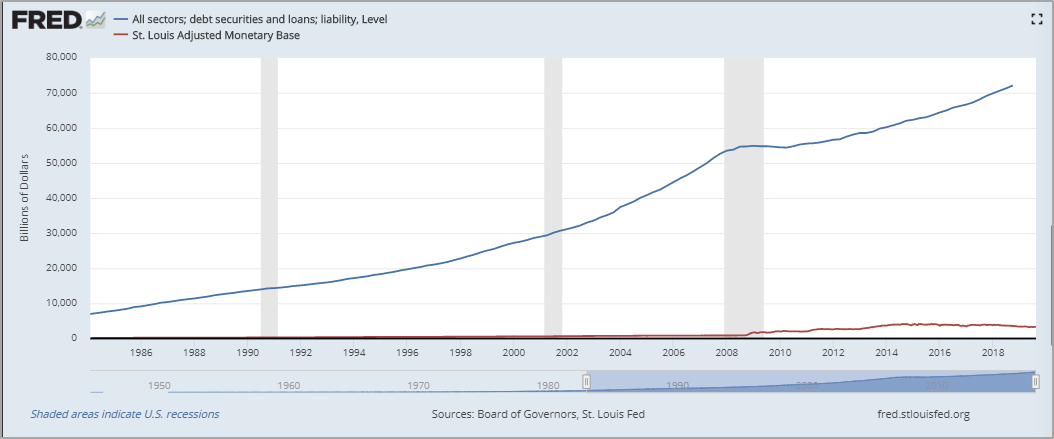
The graph of the ratio of US government debt to the monetary base. : FRED
The system as a whole owed more dollars thanexists in nature, which creates the conditions for a very high current demand for dollars. If consumers do not pay their debts, they will be taken away from their house or car. If a company does not pay its debts, its assets will be transferred to creditors through a bankruptcy process, and the share capital may be completely erased. If the government does not pay its debts, its basic functions may be suspended due to lack of funding. In most cases, failure to get dollars to pay off debt means losing your last shirt. Debt ultimately stimulates demand for dollars. While dollars are rare compared to the amount of outstanding debts, the dollar remains relatively stable.
This is how the Fed’s economy works: credit stimulation creates a source of future demand for foreign currency.In a way, it resembles drug trafficking. If a person is addicted to the drug you sell, he will buy more each time. In this case, a drug is a duty that makes everyone spin like a squirrel in a dollar wheel.
The problem with the Fed (and the dollar) economy is that itdepends on the functioning of the credit system with great leverage. And in order to support it, the Fed must increase its dollar base. That is the essence of quantitative easing. To maintain the amount of debt in the system, the Fed needs to systematically increase the supply of real dollars, otherwise the credit system will collapse. An increase in the dollar base first reduces the leverage of the credit system, but in the long run it contributes to credit growth. Another consequence is the gradual devaluation of the dollar. All this is done intentionally. Ultimately, the dollar is secured by a loan, because a loan is in fact a right of demand for real assets and, therefore, livelihoods. If you don’t bring dollars in the future, you risk losing your home, which is incredibly motivating to work for dollars.

US Federal Reserve Building
It is on the connection between dollars and dollarthe Fed keeps the game on credit, and central bankers believe that it can go on forever. Create more dollars - create more debt. Too much debt? Create even more dollars, etc. Ultimately, in the Fed (or any central bank) economy, currency is a safety valve. Since there are only $ 1.6 trillion of real dollars in the US banking system with $ 73 trillion of debt, even more dollars will need to be added to the system to support debt. It is the rarity of dollars in comparison with the demand for them that gives the dollar its value. And nothing else. The dollar is not backed up by anything else. And although the dynamics of the credit system creates the relative rarity of the dollar, its absolute rarity is becoming less and less.
Too much debt → Make more money → More debt → Too much debt
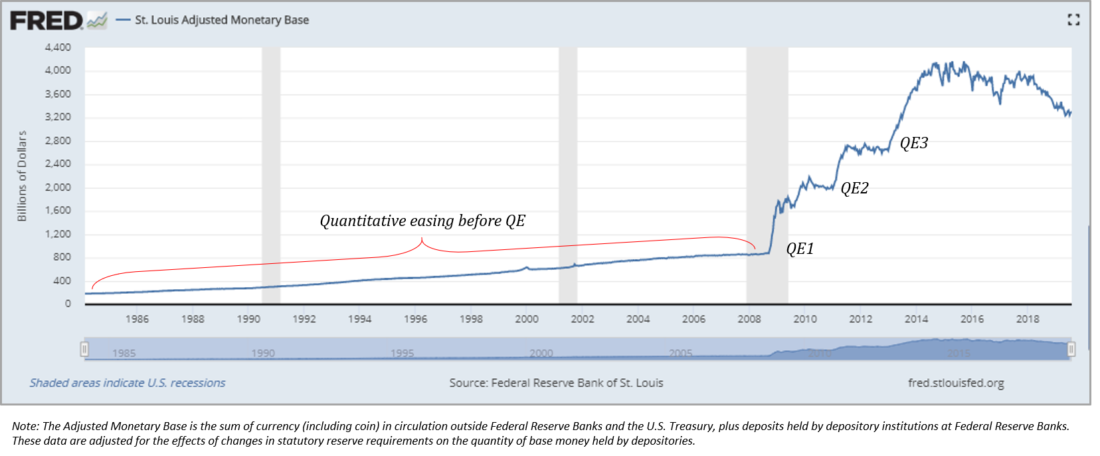
Graph of changes in the monetary base with eachquantitative mitigation (QE).
: Federal Reserve Bank of St. Lewis
As with any monetary asset, the dollarprovided with rarity, but the dollar is rare only in relation to the amount of existing dollar debt. And now he has a real competitor in the face of Bitcoin. The dollar system, with its lack of inherent monetary properties, contrasts sharply with the original and developing monetary properties of bitcoin. The rarity of the dollar is relative; Bitcoin's rarity is absolute. The dollar system is based on trust; Bitcoin - no. The central bank controls the supply of the dollar, while the bitcoin supply is controlled by the consensus of market participants. The dollar supply will always be tied to the size of the credit system, while the offer of bitcoin with a loan is not connected in any way. And the costs of creating dollars are close to zero, while the costs of creating bitcoins are tangible and constantly growing. Ultimately, the monetary properties of Bitcoin are improving and becoming less vulnerable to manipulation, while the dollar is by its nature more and more susceptible to manipulation.
Money and Digital Rarity

When valuing Bitcoin as money, the greatestthe psychological difficulty is its digital nature. Bitcoin is intangible, which is not immediately easy to comprehend. How can something completely digital be money? Although the dollar is predominantly digital, it is still more tangible to many than Bitcoin. While the digital dollar evolved from its paper predecessor and physical dollars are still in circulation, Bitcoin is originally digital. In the case of the dollar, there is a physical image that allows us to associate it with the tangible world, whereas in the case of Bitcoin there is none. Although Bitcoin hasmuch more reliable monetary propertiesthan the dollar, the dollar has always been money (formost of us), and as a result, its digital version is more intuitive. Despite the fact that the dollar has a long history of use as money and its digital version may seem more tangible, bitcoin is an ultimate rarity. The dollar supply, on the other hand, is unlimited.
Don't forget that the dollar has noown monetary properties. On its path to becoming a global reserve currency, it relied on the monetary properties of gold, but the dollar itself has no unique properties that make it a stable form of money other than its relative scarcity within a credit-linked monetary system. When evaluating Bitcoin, the first fundamental question to consider is whether something digital can share the essential properties that made gold a store of value (and a form of money).Has gold become money because it is physical or due to some other property? Why is gold among all physical objects?Gold became money not because itphysical, but thanks to a unique combination of qualities. First of all, gold is rare, fungible and very durable. Although gold has many properties that make it superior to all the money that preceded it, its main drawback was the difficulty of transportation and vulnerability to centralization, which is why the dollar came to be used along with it.
“As a thought experiment, imagineitself a metal, as rare as gold, but with the following properties: dull gray color, conducts electricity poorly, not very hardy and at the same time not very malleable and ductile, not suitable for any practical or decorative purposes, but at This has one special, magical quality - it can move through communication channels.” – Satoshi Nakamoto (August 27, 2010)
Bitcoin has the same monetary properties aswhich allowed gold to become a currency, but also solves the shortcomings of gold. While gold is relatively rare, Bitcoin has finite scarcity. Both are fungible and very durable, but gold is difficult to verify while Bitcoin is easy to verify. Gold is difficult to move and is highly centralized. Bitcoin is easy to move and is highly decentralized. In essence, Bitcoin combines the desirable characteristics of physical gold and the digital dollar, but without their critical disadvantages. When valuing funds, fundamentals are of fundamental importance. Ignore the findings or conclusions and first ask yourself:if bitcoin is really rare and finite,despite the fact that it is digital, can it serve as an effective indicator of value and make it a means of saving? Is the rare property strong enough for Bitcoin to become money, despite its digital nature?

Money can be intangible, but if it isuseful in trade, then they will be in demand. Money is a tool with which we determine the relative value of more common consumer and capital goods. This is a product that coordinates all economic activity. The absolute amount of money is not so important as the fact that it is rare and measurable. Rarity is the most important property of money. If the supply of a measuring unit is constantly and unpredictably changing, it is very difficult to measure the value of goods relative to it, and that is why rarity in itself is an incredibly valuable property. Although the cost of a measurement unit relative to goods and services may fluctuate, the stability of the money supply reduces the amount of noise in price signals.
Despite its digital nature, Bitcoin is designed to be completely scarce and therefore has the potential to become an effective form of money (and measure of value).Only 21 million bitcoins will be created, and this is a very small number as inrelative, and in an absolute sense. The Fed can create $ 100 billion at the push of a button. That's about $ 5,000 for every bitcoin that will ever exist.
In order to provide a wider context: The Fed, the Bank of Japan and the European Central Bank since the last financial crisis together created new money for $ 10 trillion, or about $ 500,000 for one bitcoin. And the dollar, and the euro, and the yen, and bitcoin are digital, but bitcoin among them is the only noticeably rare and originally possessing monetary properties.
But it is not enough to simply say that Bitcoincertainly rare, and no one should just take it for granted. It is important to understand how and why this is so. Why can't more than 21 million Bitcoins be created and why can't it be copied? Why is Bitcoin secure and why can't it be manipulated? Although a combination of many components allows Bitcoin to operate with a securely fixed supply, the Bitcoin network has three key pillars of security that are intertwined with each other and supported by the economic incentives of the currency itself:
- network consensus and full nodesensure compliance with general management rules;
- mining and proof of work (PoW)are responsible for confirming the transaction history and giving Bitcoin security a physical basis;
- private keysprotect the measurement unit and ensure independence of ownership from confirmation.
What makes Bitcoin safe
Network Consensus and Complete Nodes

21 million is not just a guaranteed numbersoftware. Bitcoin's fixed supply is driven by a consensus mechanism, and all market participants have an economic incentive to comply with the rules of the Bitcoin network. Although theoretically the consensus of the Bitcoin network can increase the supply to more than 21 million, for this the vast majority of users must agree to depreciate their currency. In practice, the global and decentralized network of rational economic participants in the voluntary monetary system will not form a consensus on the depreciation of the currency, which they all independently and voluntarily decided to use as a means of saving. This is the reality that supports economic incentives, the technical architecture, and the network effect of Bitcoin.
A complete Bitcoin node is a computer or server,storing the full version of the Bitcoin blockchain. Complete nodes independently compose a blockchain version based on a common set of consensus rules. Although not everyone who holds bitcoins has a full node, it is accessible to everyone, and each node checks all transactions and blocks. Everyone who supports a full node has access to the Bitcoin network and can broadcast transactions (or blocks) without needing permissions. Nodes must not trust other nodes. Each node independently checks the complete Bitcoin transaction history based on a common set of rules, which allows the network to arrive at a consistent and accurate version of the history without the need for trust.
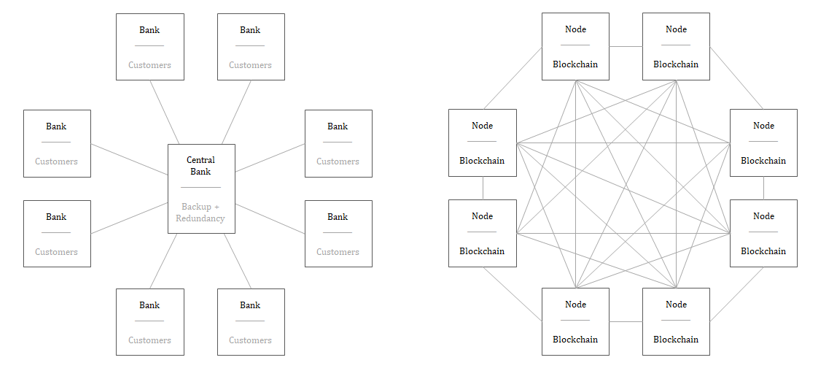
Comparison of centralized (left) and decentralized monetary system (right).
: Unchained Capital
With this mechanism, the Bitcoin networkeliminates the need to trust a centralized third party and strengthens the reliability of a fixed offer. All nodes store a history of all transactions, which allows each node to determine the validity of any future transaction. In total, Bitcoin is the most secure computing network in the world, because everyone has access to it and no one should trust anyone. The network is decentralized and does not have a single point of failure. All nodes act as a system of checks and balances for the rest of the network, and without a central source of truth, the network is resistant to attacks and distortion. Failure or distortion can occur at any node, but the rest of the network will remain untouched. The more nodes, the more decentralized Bitcoin is and the more difficult it is to distort or censor the network.
Each full node provides executionnetwork consensus rules, the critical element of which is a fixed offer. Each block involves the issuance of a given number of bitcoins, and each transaction must originate from a previous valid block to be valid. Every 210,000 blocks, the number of Bitcoins issued in each valid block is halved until it eventually reaches zero around 2140. Thus, the supply schedule has an asymptotic, limited character. Since each node independently verifies every transaction and every block, the network collectively guarantees a fixed supply of 21 million. If any node broadcasts an invalid transaction or block, the rest of the network will reject it and that node will fall out of the consensus. Essentially, any node can try to create excess bitcoins, but all other nodes have an incentive to ensure that the supply of bitcoin meets a predetermined limit, otherwise the currency will be arbitrarily devalued directly at the expense of the rest of the network.
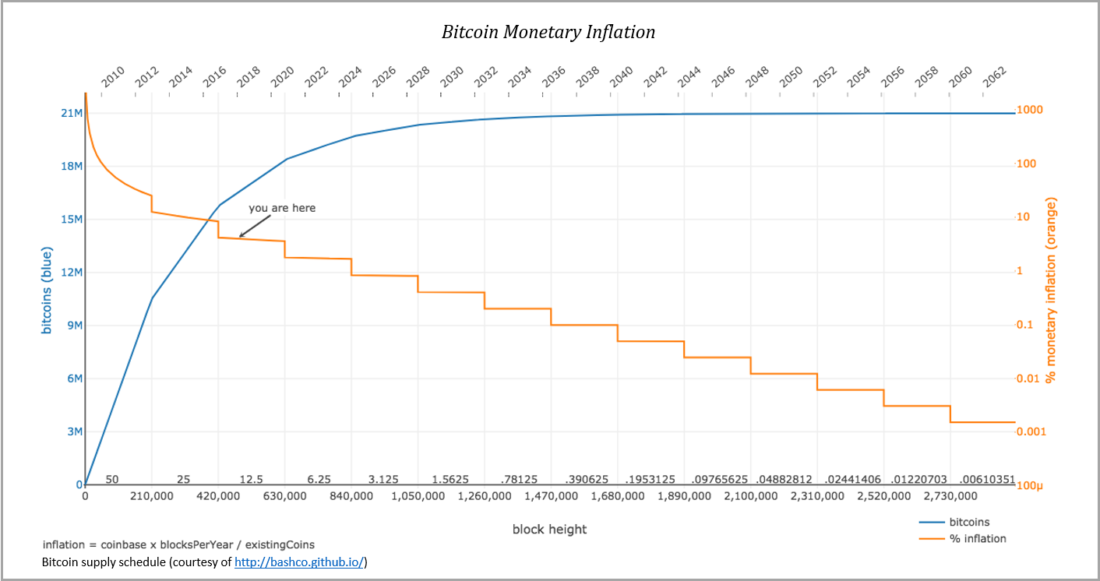
Bitcoin monetary inflation.
: bashco.github.io
Also, any network member or an outsider cancopy the Bitcoin software to create a new version, but the nodes operating on the Bitcoin network will consider any units created by such a copy to be invalid. No one will accept a currency like Bitcoin. Each Bitcoin node independently checks whether that other unit is Bitcoin, and any copy will be invalid, since it does not come from the previous valid Bitcoin block. It would be like trying to give money out of the Monopoly game for dollars. No matter how you want it, no one will accept such a copy as Bitcoin, and it will not have the properties of a Bitcoin network. Having a complete node allows you to instantly check if Bitcoin is valid, and any copy of Bitcoin will immediately be identified as a fake. The consensus of the nodes determines the actual state of the network in a closed system; everything that happens outside it is like it never happened.
Mining and Proof of Work (PoW)

illustrations: BitNews
Within the consensus mechanism, some nodes(called miners) perform the function of proof of work by adding new Bitcoin blocks to the blockchain. This function checks the complete transaction history and confirms current transactions. The mining process gives Bitcoin security a physical basis. To create blocks, miners have to perform trillions of cryptographic calculations that require the expenditure of significant energy resources. When a block is found, it is offered to the rest of the network for confirmation. All nodes (including other miners) check whether the block is valid based on the general set of network consensus rules, which were mentioned above. If any transaction in the block is invalid, then the entire block is invalid. Also, if the proposed block is not based on the last valid block (i.e., the longest version of the blockchain), then this block is invalid.
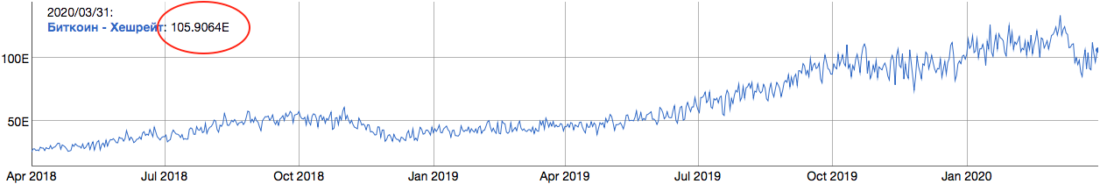
Graph of the entire processing power of the Bitcoin network as of March 31, 2020. : bitinfocharts.org
At 105.9 exahash/s the Bitcoin network consumesapproximately 9 GW of electricity, or ~$11 million per day (~$4 billion per year) at a cost of 5 cents per 1 kWh (rough estimate). A new block is created approximately every 10 minutes, which equates to approximately 144 blocks per day. Creating each block costs the network as a whole approximately $75,000, and the reward per block(12.5 new bitcoins, not including transaction fees)at a Bitcoin price of $8000 is approximately$100,000. The higher the cost of searching for a block, the more expensive an attack on the network will be. Block search costs are the tangible resources required to record Bitcoin's transaction ledger. As the network grows, it becomes more fragmented and the total amount of compensation to miners increases. From a game theory point of view, the greater the competition and the higher the opportunity costs, the lower the likelihood of collusion, since the work of miners is checked by all network nodes, constantly acting as a system of checks and balances.
Remember also that with every validthe block emits a certain number of bitcoins (up to 21 million). Bitcoins issued with each block and network transaction commissions compensate miners for performing the function of proof of work. Miners get paid in bitcoins for network security. When creating the proposed block, miners include the release of a certain number of bitcoins in it as compensation for spending real, tangible resources on securing the network. If the miner turns on the amount of bitcoins that is not consistent with the predefined offer schedule, the rest of the network will reject the block as invalid. As part of security, in order to receive compensation, miners must check and guarantee a fixed offer. Miners risk their own skin in the form of capital costs (and energy consumption), and the invalid block is left without reward.
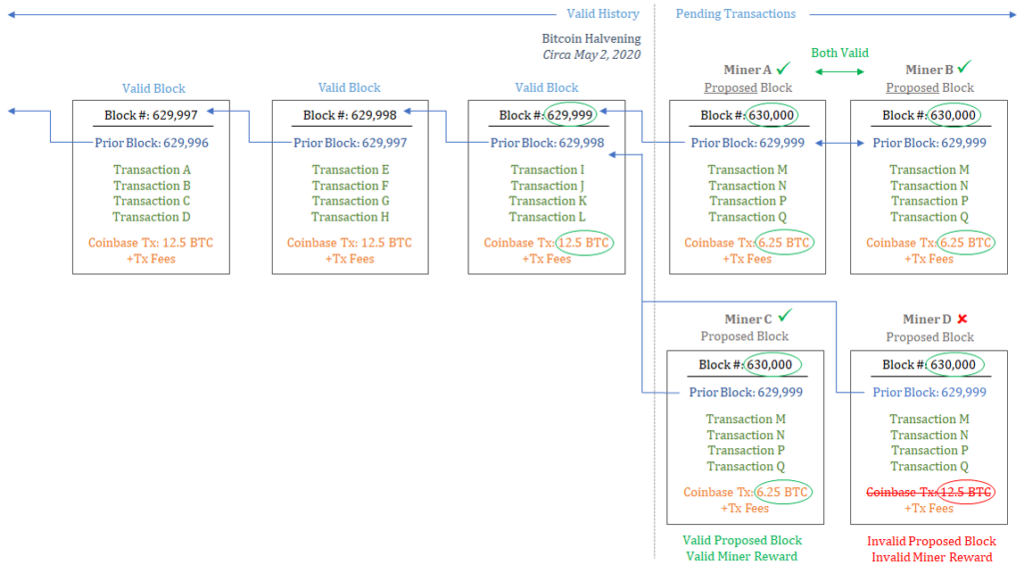
Scheme of halving the remuneration for mining Bitcoin. : Unchained Capital
The actual reward paid to miners is halved every 210,000 blocks, with the next halving scheduled for block 630,000 (around May 2020).

Then the reward will decrease from 12.5 to 6.25Bitcoin per block. If subsequently one of the miners turns on an invalid reward (other than 6.25 bitcoin), the rest of the network will reject such a block. Halving is important not only because the number of new bitcoins emitted is decreasing, but also because it shows that the economic incentives of the network continue to effectively coordinate and guarantee a fixed supply of currency on a fully decentralized basis. If one of the miners tries to cheat, the rest of the network will punish him as much as possible. This behavior is coordinated solely by the economic incentives of the network. The fact that this happens on a decentralized basis, without any central authority, enhances network security.
Since mining is decentralized and all minersconstantly competing with each other, conspiring for miners is impractical. In addition, the work of miners is checked by all nodes, instantly and almost at no cost, which creates very powerful checks and balances, separated from the mining function as such. Creating blocks is expensive, but checking is easy. This is the fundamental difference between Bitcoin and the monetary systems with which it competes, whether it is gold or the dollar. And compensation to miners for network security and fixed offers are paid exclusively in bitcoin. The economic incentives of the currency (compensation) are so strong, and the penalties are so strict and so easy to implement that miners are as motivated as possible to collaborate and do real work. Due to the tangible costs of the mining process, the inclusion of the offer schedule in the confirmation process (with the participation of all nodes) and the separation of the mining function from ownership, the network as a whole reliably and constantly guarantees a fixed currency offer (21 million) without the need for trust and with the opportunity to reach consensus on decentralized basis.
Private keys and equal rights

: Unsplash
While miners create and propose blocks, andnodes verify the work they have done, private keys control access to the actual units of value. Private keys control rights to 21 million bitcoins(only 18.3 million mined so far). Bitcoin has no personal data; Bitcoin is nothingknows about the outside world. The Bitcoin network checks signatures and keys. And it's all. Only someone who controls the private key can create a valid Bitcoin transaction with a valid signature. Actual transactions are included in the blocks created by the miners and verified by each node, but only those who own private keys can conduct valid transactions.
When a valid transaction is broadcast,Bitcoins are spent (sent) to a specific public address. Public addresses are based on public keys, which are based on private keys. Public keys and public addresses can be calculated using a private key, but a private key cannot be calculated using a public key or public address. This is a one-way function protected by strong cryptography. Public keys and public addresses can be shared without revealing anything about the private keys. When Bitcoins are sent to a public address, they are actually locked in a safe, and in order to open that safe and spend the Bitcoins, you must provide a valid signature with the corresponding private key(each public key and public address has a unique private key). The owner of the private key providesunique signature without revealing a secret. The rest of the network can make sure that the holder of the private key has provided a valid signature without knowing any details about the private key itself. Pairs of public and private keys are the foundation of Bitcoin. And, ultimately, it is private keys that control access rights to the economic value of the network.
It doesn't matter if you have one tenthbitcoin or ten thousand bitcoins. Each unit is protected and verified using the same mechanism and the same rules. Everyone has equal rights. Regardless of the economic value, each bitcoin (and address) is treated equally in the Bitcoin network. If a valid signature is provided, then the transaction is valid and will be added to the blockchain (subject to payment of a commission). If an invalid signature is provided, the network will reject the transaction. It does not matter whether a particular participant is somewhat powerful or weak. Bitcoin is apolitical. It only checks keys and signatures. The one with the most bitcoins can pay a higher commission to increase the priority of the transaction, but all transactions are confirmed based on the same set of consensus rules. Miners determine the priority of a transaction based solely on cost and benefit. If transactions are equally valuable, then priority will depend on the time sequence. But it’s important that the mining function that confirms the transactions is separate from ownership. Bitcoin is not a democracy. Ownership is controlled by keys, and every Bitcoin transaction is confirmed based on the same network criteria. It is either valid or not. And each bitcoin, in order to be valid, must come from a block that is consistent with the schedule of the 21 million offer.
This is why it is so important in Bitcoin that users control the keys. Bitcoins are extremely rare, and the transfer of each Bitcoin is controlled by private keys. There is a saying:not your keys - not your bitcoins. If your keys are controlled by a third party,such as a bank, it controls your access to the Bitcoin network and can easily limit or confiscate your funds. Although many people prefer trusting intermediaries, Bitcoin’s security model is unique: everyone can not only control their private keys, but also use the network without having to obtain permissions and transfer funds to anyone anywhere in the world. This is only possible if the user controls the private key. User control over private keys decentralizes control over the economic value of the network, which increases network security. The more distributed the access to the network, the more difficult it is to distort or capture the network. In addition, when a user holds a private key, it is extremely difficult to restrict access to him or confiscate his funds. Each bitcoin in circulation is protected by a private key. Miners and nodes guarantee that only 21 million bitcoins will exist, but the private keys of their owners control and protect the existing bitcoins.
Bitcoin in perspective

So, the offer of bitcoin is controlled by the networkby consensus mechanism, and miners perform the function of proof of work, giving Bitcoin security a physical basis. As part of the security function, miners get paid in bitcoins for creating blocks that check the history and confirm current transactions. If the miner tries to charge itself an amount that is not consistent with the fixed offer of bitcoin, the rest of the network will reject its work as invalid. The currency offer is integrated into the Bitcoin security model, and in order for miners to receive compensation, you need to spend real energy resources. Nevertheless, the work of all miners is checked by each node of the network, so that no one can cheat without the real risk of punishment. Bitcoin's consensus mechanism and verification process ultimately controls the transfer of ownership of the network, but ownership is controlled and protected by private keys owned by network users.
Set aside prejudices about whatmoney, and imagine a currency system with a guaranteed rare and fixed offer. Anyone can join the network without the need for permission and forward transactions to anyone anywhere in the world. Anyone can also easily and independently verify the currency offer and ownership of the network. Imagine a global economy where billions of people scattered around the world can conduct transactions in a single decentralized network and come to the same consensus regarding ownership of the network without coordination by any central authority. How valuable will such a network be? Bitcoin is valuable because it is finite, and finite because it is valuable. Economic incentives and a network management model reinforce each other. The general consequence is a decentralized, trust-free global monetary system with a fixed supply, accessible to everyone.
Since Bitcoin has the original anddeveloping monetary properties, it differs from all other digital money. While the supply of Bitcoin remains fixed and of course scarce, central banks are forced to expand the monetary base to support their old system. Bitcoin will become more and more attractive as more and more market participants understand that future quantitative easing is not just a tool of central banks, but a necessary function to support a worse alternative. Before Bitcoin, everyone was forced to use this system by default. Now Bitcoin offers a viable alternative. Every time the Fed starts QE again to support the credit system, more people will realize that the monetary properties of Bitcoin are much better than those of the old systems, be it the dollar, the euro or the yen. Which is better - A or B? Time will show. In global monetary competition, Bitcoin has monetary qualities that the fiat monetary system lacks. Ultimately, Bitcoin is backed by the same thing as any money:the reliability of their monetary properties.
</p>
