Today we bring to your attention the first article in a series dedicated to thinking about the basicsBitcoin and cryptocurrencies in general. Do not forget to follow the updates, so as not to miss the subsequent articles from the series.
You heard from seemingly smartfriend, that he is not sure about Bitcoin, but believes in blockchain technology? This is like saying that you believe in airplanes, but are not sure of the wings, and it is highly probable that anyone who thinks so does not understand the topic. In fact, Bitcoin and blockchain are interdependent. However, it can be incredibly difficult for a beginner to figure out how it all works. Honestly, this can be overwhelming: considering the complexity and number of projects, who has the time to analyze all this? There is still a convenient way, but you need to know where to start. Although there are thousands of cryptocurrencies and blockchain initiatives, only one really matters: Bitcoin. First, ignore everything else, as if it did not exist, and try to understand why Bitcoin exists and how it works. This will be the best foundation, which then allows you to consider everything else.
</p>It is also the most practical entry point. Before risking your hard-earned money, take the time to understand Bitcoin, then apply this knowledge to analyze the entire field. There are no guarantees that you will come to the same conclusions, but most often those who devote time to intuitively understand how and why Bitcoin works, it is easier to recognize the flaws inherent in this area. And even if not, starting with Bitcoin is still the best chance to make a competent and independent assessment. Ultimately, Bitcoin does not come down to making money or a quick money-making scheme. Its essence is to preserve the value you have already created, so you should not risk it without the necessary theoretical base. In the world of digital currencies, Bitcoin has the longest history that can be estimated, and most of all educational resources, and that is why Bitcoin is the best tool for learning.

Books about Bitcoin. Images: Unchained Capital
Before embarking on this journey,it should be understood that Bitcoin was created with the specific goal of solving the existing problem of modern money. The creator of Bitcoin intended to create a peer-to-peer digital cash system without the need for a trusted third party, and blockchain is a critical part of the solution. In practice, bitcoin as a currency and its blockchain are interdependent. One does not exist without the other: Bitcoin needs a blockchain in order to function, but a functioning blockchain would not exist without an internal currency that properly stimulates the use of resources to protect it. This domestic currency must be a viable form of money, because it provides security, and for this it must have reliable monetary properties.
There is no security without money, and without securitythe value and immutability of the blockchain will collapse. For this reason, the blockchain is useful only within the framework of monetary use, and money does not grow on trees. Yes, everything is so simple. Blockchain is only good for one thing - eliminating the need for a trusted third party, which only works in the context of money. The blockchain cannot regulate anything that exists outside the network. Although the blockchain is able to track ownership outside the network, it can only regulate ownership of the internal currency of its network.
Bitcoin monitors and regulates lawproperty. If the blockchain is unable to do both, any records that it keeps will be inherently unprotected and subject to change. In this sense, immutability is not an integral feature of the blockchain, but an emergent property. And if the blockchain is not immutable, then its currency will never be a viable form of money, because the transfer and final payment will not be possible to a reliable degree. Without reliable settlements, the monetary system is dysfunctional and will not attract liquidity.
Ultimately, monetary systems converge toone remedy, because their utility in liquidity, and not in consumption or production. And liquidity is consolidating around the safest, long-term means of savings. It would be irrational to store money in a less secure, less liquid monetary network if a safer and more liquid network is available. The general conclusion is that only one blockchain is viable and, ultimately, necessary. All other cryptocurrencies compete for the same use as Bitcoin - use as money. Not everyone realizes this, but value continues to consolidate around Bitcoin, because it is the safest blockchain and everyone competes for the same application. The assimilation of these concepts provides a foundation for understanding Bitcoin, which then allows you to consider and evaluate the noise outside of Bitcoin. With a basic knowledge of how Bitcoin actually works, it becomes clear why there is no blockchain without Bitcoin.
Blockchain does not exist

Often, Bitcoin's transaction registry is represented asa public blockchain that lives somewhere in the cloud, like a kind of digital public space where all transactions are collected. However, there is no single source of truth. There are no oracles, no central public blockchain where everyone independently makes transactions. Instead, each member of the network designs and maintains their own independent version of the blockchain based on a common set of rules. Nobody trusts anyone and everyone checks everything. Everyone can come to the same version of truth without having to trust any third party. This is the essence of how Bitcoin solves the problem of removing intermediaries from the digital cash system.
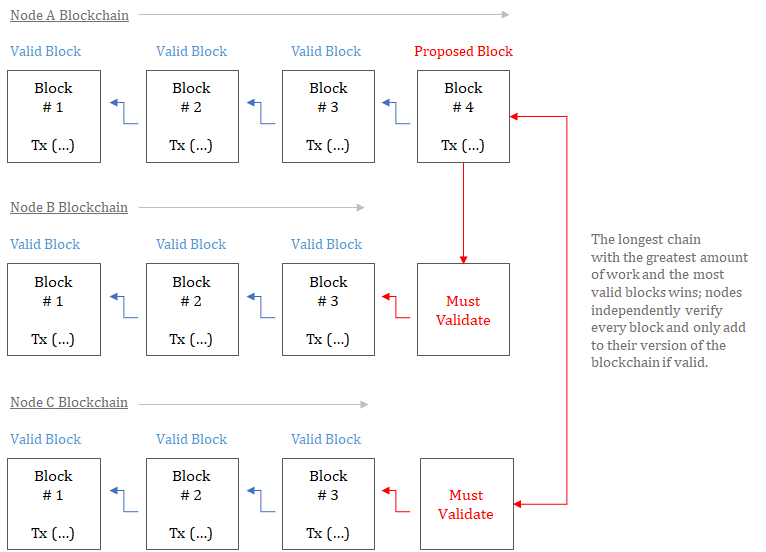
Validation scheme of nodes (nodes) in the Bitcoin blockchain. Images: Unchained Capital
Each participant supporting a node on the Bitcoin network independently verifies every transaction and every block.At the same time, each node forms its own independent version of the blockchain.Consensus is reached in the network because every node verifies every transaction(and each block)based on a basic set of rules(and the longest chain wins). If a node broadcasts a transaction or block, do notsatisfying the consensus rules, other nodes will reject them as invalid. Thanks to this function, Bitcoin is able to do without a central third party. The network converges on the same coordinated state of the blockchain, and no one trusts any third party. Nevertheless, the currency plays a key role in coordinating the Bitcoin consensus mechanism and streamlining the blocks, which ultimately represents the complete and valid transaction history of Bitcoin (or its blockchain).
Bitcoin Basics: Blocks and Mining
A block can be thought of as a dataset that connects the past to the present.In a technical sense, individual blocks record changes in the overall state of bitcoin ownership over a specific time period.Collectively, the blocks record the entire history of Bitcoin's transactions, as well as the ownership of all Bitcoins at any given momentThe way blocks are built, computed, and validated is critical to the network consensus process, as well as ensuring that the state changes are recorded.BTC Fixed Supply (21 million): Miners compete to create and compute blocks, which are then offered for acceptance by the rest of the network.For simplicity's sake, you can think of the mining function as a continuous process of checking the history and completing the queued Bitcoin transactions.With each block, miners add new transactions to the blockchain and verifyIt is through this process that miners ensure the security of the network.However, all nodes in the network then check the work done by the miners to ensure network consensus.In technical terms, miners create blocks representing a dataset that includeThree Critical Elements(again, in simplified form):
- Referring to the previous block → checking the blockchain history.
- Bitcoin transactions → completion of transactions from the queue (change of ownership status).
- Transaction coinbase + commission → compensation to miners for network security.
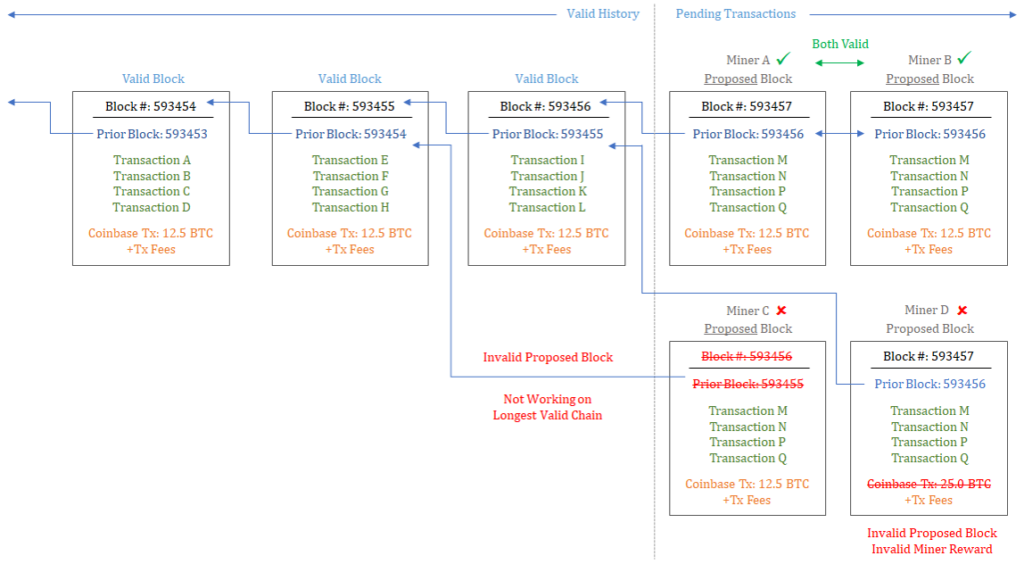
To calculate blocks, miners do this:called the proof of work function (PoW or «proof of work»), spending energy resources. For blocks to be valid, all inputs must be valid and each block must satisfy the current complexity of the network. To satisfy the complexity of the network, a random value is added to each block(called nons), after which the combined data set is run through Bitcoin's cryptographic hashing algorithm(SHA-256). The resulting output (or hash) to bevalid must match the complexity of the network. You can imagine this as a simple enumeration function, only, from the point of view of probability theory, in order to find real evidence for each proposed block, you need to sort out trillions of random values. Adding a random nonse might seem redundant. However, it is this function that makes miners spend significant energy resources in order to calculate the block, which ultimately makes the network more secure, since an attack on it will be extremely expensive.
Due to the addition to the proposed block, throughoutotherwise representing a static data set, a random nonce, each resulting output (or hash) is unique. When checking each nonce, the resulting output has an equally low probability of matching the network complexity(i.e., the probability of being valid evidence). Although often referred to as extremelydifficult mathematical problem, in fact, the difficulty lies only in the fact that the search for real evidence requires enumeration of trillions of possible solutions. There are no short cuts; it is necessary to expend energy. Valid evidence is easily verified by other nodes, but it cannot be computed without spending a large amount of resources. With the addition of new computing resources to the network, the complexity of the network increases, requiring iterating over more values and spending more energy resources to calculate each block. In essence, miners incur material costs for calculating blocks, but all other nodes can then test their operation very easily and practically without costs.
In total, the structure of stimuli allowsnetworks reach consensus. Miners must bear significant costs for network security, but receive rewards only if they do the actual work; and the rest of the network can directly determine whether the work is valid, based on consensus rules and without incurring costs. There are several consensus rules, but if a transaction in a block is invalid, then the entire block is invalid. For a transaction to be valid, it must come from a previous valid Bitcoin block and cannot duplicate a previously spent transaction. To be valid, each block must be based on the most current version of the story, and must also include a valid coinbase transaction. The coinbase transaction rewards miners with new bitcoins for network security, but it is only valid if the work done is valid.
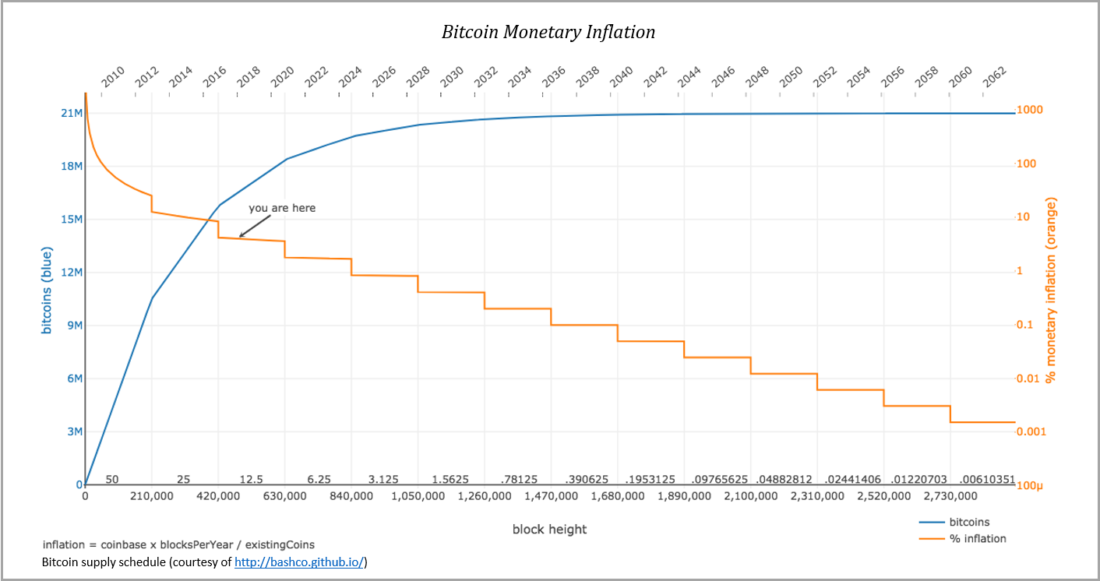
coinbase rewards are managedpredetermined supply schedule, and currently 12.5 new Bitcoins are issued with each valid block. In May 2020, the reward will be halved to 6.25 Bitcoin and then every 210,000 blocks(or approximately every 4 years)will continue to halve untilwill reach zero. If miners include an invalid reward in a proposed block, the rest of the network will reject it, which represents the underlying mechanism governing the limited total supply of 21 million bitcoins. However, software alone is not enough to guarantee a fixed supply or an accurate ledger of transactions. Everything depends on economic incentives.
Decentralized consensus

Why is this so important? Within one integrated function, miners check history, confirm transactions and receive payment for security without the need for trust. The immutability of Bitcoin's fixed offer is built into its security function, and since the network independently checks the operation, it is possible to achieve consensus on a decentralized basis. If the miner does the actual work, he can rely on what will be rewarded without having to trust anyone. Conversely, if a miner does an invalid job, the rest of the network applies the rules, effectively keeping the payout until the actual job is done. And the offer of currency is one of the conditions of reality. If the miner wants to receive a reward, he must also provide a fixed currency offer, which maintains network consistency. The currency incentive system is so strong that everyone is forced to follow the rules, which contributes to a decentralized consensus.
If the miner calculates and offers invalidblock, in particular, including either invalid transactions or invalid coinbase reward, the rest of the network will reject it. In addition, if the version of the miner's history does not represent the longest chain with the greatest proof of the work, any proposed block will also be considered invalid. In fact, as soon as the miner saw a new valid block proposed on the network, he should immediately start working on top of this block, otherwise he risks falling behind and performing invalid work, incurring irreparable costs. That is, having performed an invalid work, the miner will incur real costs, but will not receive any compensation for this.
Bitcoin governance. pic.twitter.com/mrzBPg6LjL
— Michael Goldstein (@bitstein) August 26, 2017
Thanks to this mechanism, miners are highly motivated to always perform honest, valid work within the blockchain consensus:either get a reward or nothing. Also for this reason, the higher the costs ofdoing the job, the more secure the network becomes. The more energy it takes to write or rewrite Bitcoin's transaction history, the less likely it is that some miner will sabotage the network. The motivation to cooperate is higher the more expensive the work, which would otherwise be considered invalid by the rest of the network. As the network becomes more secure, Bitcoin becomes more valuable. As the value of Bitcoin and the cost of computing blocks increases, the motivation to do actual work increases.(more income, but more costs), and the penalty for invalid work becomes more significant(more costs, but no income). Why don't miners collude?First of all, they can't. Secondly, they tried. But third, the fundamental reason is that as the network grows, it becomes more fragmented and the economic compensation that miners collectively receive increases. From a game theory perspective, increased competition and opportunity costs make collusion more difficult, and the verification of miners' work by all nodes in the network serves as a constant system of checks and balances. Miners simply get paid for providing a service, and the more miners there are, the greater the incentive to cooperate, because as competition increases, so does the likelihood of punishment for invalid work. Remember also the random value -nons. Although seemingly unnecessary, it underlies a function that requires the expenditure of energy resources. It is these tangible costs(skin in the game)combined with the value of the currency motivates actual work and allows the network to reach consensus.
Since all nodes on the network independently validate blocks and miners are penalized to the maximum for invalid work,the network is able to reach a consensus regarding the exact state of the blockchain without relying on any single source of knowledge or truth. Such decentralized coordination does notIt would be possible without Bitcoin as a currency. The Bitcoin network should reward miners for security with its domestic currency, whether primarily in the form of new bitcoins today or exclusively in the form of transaction fees in the future. If the compensation paid to the miners is not considered a reliable form of money, then there will be no motivation to invest in the work.
The role of money in the blockchain
If the main(and especially the only one)the utility of an asset lies in exchange for other goods and services and if it is not linked to the income stream of a productive asset(such as stocks or bonds)then it must compete as a form of money andwill retain value only if it has reliable monetary properties. Bitcoin is a bearer asset with no utility other than exchange for other goods and services. It is also not linked to the income stream of productive assets. Therefore, Bitcoin is only valuable as a form of money and only retains value by having valid monetary properties. By definition, this applies to any blockchain. All any blockchain can offer in exchange for security is an on-chain monetary asset without any mandatory off-chain payment requirements, which is why a blockchain can only be useful in relation to monetary applications.
Without an internal currency, the security of a blockchain depends on trust, eliminating the need for a blockchain itself. Bitcoin's security feature in practice(mining), protecting the validity of the blockchain without the need for trust, requires significant capital investment in addition to high marginal costs(Energy consumption). To recoup this investment and secure the futureThe returns, the Bitcoin payouts, must more than offset the total costs, otherwise no one will invest. Essentially what miners get for protecting(bitcoins), must be a reliable form of money in order to stimulate investment in security.
It is also fundamentally important for motivationala consensus framework on the network. Miners have built-in motivation not to sabotage the network, as this will directly undermine the value of the currency in which they receive compensation. If Bitcoin were not valued as money, there would be no miners, and without miners there would be no blockchain worth protecting. Ultimately, miners get paid to protect the reality of the blockchain. If the network is unable to reach a reasonable consensus and if property rights are subject to change, then no one can rely on Bitcoin as a value-sharing mechanism. The value of the currency ultimately protects the blockchain, and the immutability of the network is the basis of the value of the currency. This is a relationship interdependent in its essence.
Immutability - an emergent property
Immutability is an emergent propertyBitcoin, not a feature of the blockchain. A global decentralized monetary network without central governance cannot function without an immutable ledger(i.e. if the blockchain history is unprotected and subject to change). If calculations are with a unit of value (bitcoin)cannot be reliably considered final, then no one will exchange real value for it. As an example, consider a scenario where one party bought a car from the other with bitcoins. Let's assume that ownership of the car is transferred and the buyer physically takes possession of it. If Bitcoin's ownership registry could easily be rewritten or changed(i.e. blockchain history can be changed), the party that gave bitcoins in exchange for a car inin the end, it can stay with bitcoins and with the machine, while the other side will be left with nothing. That is why the immutability and finality of the calculations are critical to the functioning of Bitcoin.
Don't forget that Bitcoin knows nothing about the outside world. Bitcoin only knows how to issue and verify currency. Bitcoin(like any other blockchain)unable to regulate anything existingoffline; it is a completely closed system. The Bitcoin network can only confirm one side of a two-way exchange of value. If Bitcoin transfers could not be reliably considered final, then it would be functionally impossible to exchange anything of value for Bitcoin. This is why the immutability of the Bitcoin blockchain is inextricably linked to the value of Bitcoin as a currency. The finality of settlements in Bitcoin is only possible thanks to the reliable immutability of the ledger. And the ledger is reliably immutable only due to the value of the currency. The more valuable Bitcoin becomes, the greater the security; and the higher the security, the more reliable the registry.
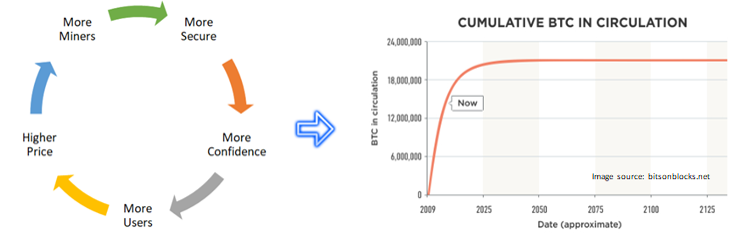
Bitcoin value cycle. Images: Unchained Capital
In the end,immutabilityis an emergent property, but it also dependsfrom other emergent properties of the network. As Bitcoin becomes more decentralized, it becomes increasingly difficult to change the consensus rules and reverse or prevent valid transactions(also called censorship). With increasing censorship, Bitcoin is growing.network trust, which contributes to adoption, further decentralizing the network, including its mining function. In fact, Bitcoin, as it grows, becomes more decentralized and resistant to censorship, which strengthens the immutability of the blockchain. It is becoming increasingly difficult to change the history of the blockchain, because each participant represents an ever smaller and smaller part of the network. No matter how concentrated the network ownership and mining are at any given time, as they grow in value, they become decentralized, as a result of which Bitcoin's immutability increases.
Bitcoin, not blockchain

Such a multi-dimensional incentive structure is complex, butIt is critical to understanding how Bitcoin works and why Bitcoin as a currency and its blockchain depend on each other. Both are tools that rely on each other. Without one another is virtually meaningless. And such symbiotic relationships only work with monetary use. Bitcoin is valuable as a form of money just because it has no other utility. This applies to any asset embedded in the blockchain. Bitcoin provides value only through current or future exchanges. And the network can perform only one final function: to verify that each specific bitcoin is really Bitcoin, and to confirm ownership. The Bitcoin network is a closed and completely independent system. Her only connection with the outside world is through a security function and transaction confirmation. The blockchain maintains a register of property rights, and the currency is used to pay for the security of this registry. It is thanks to the functionality of the currency that the network is able to provide the necessary level of security to guarantee the immutability of the blockchain, which allows network participants to more easily and more consistently reach consensus without the need to trust any third party. The cumulative result is a decentralized and trustworthy money supply network with a fixed supply, accessible all over the world and not requiring permissions.
All other fiat currencies, commodity money and cryptocurrencies compete forsame application as bitcoin, whether understood or not, andmoney systems converge to one means, because their utility in liquidity, and not in consumption or production. It would be irrational to store value in a smaller, less liquid and less secure network if a larger, more liquid and more secure network is available. Bitcoin is valuable not because of any particular quality, but because it has reached the ultimate digital rarity. This is the basis of why Bitcoin is safe as a money network, and this property depends on many other emergent properties.
Blockchain, on the other hand, is justBitcoin-related invention eliminating trusted third parties. It serves no other purpose. It is valuable only as a part of a larger puzzle and is useless if it does not function in combination with currency. The genuine rarity of bitcoin and the immutability of its blockchain ultimately depends on the value of the currency as such. Trusting an aggregate function contributes to increased adoption and liquidity, which strengthens the value of the Bitcoin network as a whole. When people choose Bitcoin, they at the same time give up the worst money networks. In fact, this is why the emergent properties of Bitcoin are almost impossible to reproduce, and its monetary qualities increase over time (and with increasing scale), also directly due to the worst money networks.
“I don’t think we will ever have againgood money if we do not tear it out of the hands of governments. That is, we can’t forcibly pull them out of the hands of governments, but we can somehow introduce something that they can’t stop. ” - F. A. Hayek
Ultimately, blockchain is only useful inmonetary application, because its security depends on the domestic currency. Bitcoin represents the most secure blockchain. Because all other blockchains compete for the same fundamental monetary use, and because Bitcoin's network effect only continues to enhance its security and liquidity, no other digital currency can compete with it. Liquidity begets more liquidity, and as a consequence, monetary systems converge toward one medium. Bitcoin's security and liquidity rendered all other cryptocurrencies obsolete before they were even born.Find a cryptocurrency approaching Bitcoin in terms of security, liquidity or the reliability of its monetary qualities - and I will find you a unicorn.
The real competition for bitcoin is the oldmoney networks, in particular dollar, euro, yen and gold. As a homework, consider Bitcoin compared to these old cash assets. Bitcoin does not exist in a vacuum; it represents an alternative to other forms of money. Evaluate it based on the relative strength of its monetary properties, and when you have a comparison of the parameters of Bitcoin and old systems, this will provide a solid foundation for evaluating any other projects related to the blockchain.
Do not forget that this is only the first part of a large series of articles on a very interesting topic. Follow the news on our website so as not to miss the sequel.
</p>