The Ethereum Foundation's website has published details of another hard fork designed to delay the activation of thecalled bomb complexity.
The update was called Muir Glacier and will be activated on block # 9200000, which is expected to be produced on January 2, 2020, depending on the speed of release of the blocks.
In a message, the lead developer of the Ethereum Foundation, Hudson Jameson, asked node holders to update their software by December 30, 2019.
A complexity bomb is complementaryProof-of-Work algorithm; Ethereum mining complexity control mechanism, increasing its value exponentially every 100,000 blocks. By increasing the time spent in blocks, the complexity bomb is also designed to encourage Ethereum ecosystem participants to switch to the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) algorithm.
Ethereum developers previously discussed the possibilitycomplete removal of this mechanism, however, in the end, agreed to postpone it, for which Muir Glacier hard fork will be held. After it, the activation of the complexity bomb will be delayed by 4 million blocks.
According to Etherscan, today the valuedifficulty is 17.15 seconds. Although this is almost half the figure of September 2017, it still leads to too long a transaction processing time.
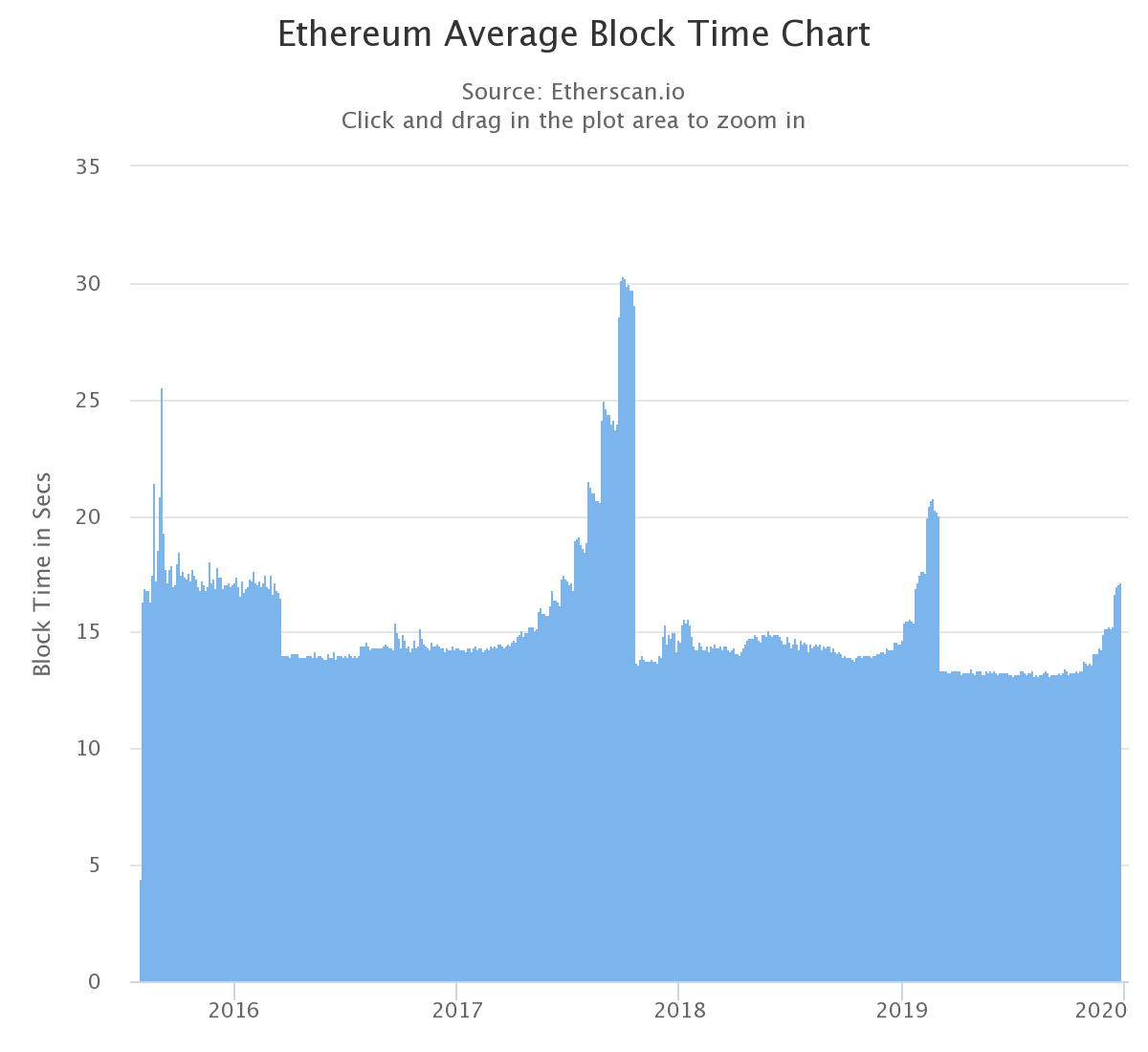
Data: Etherscan
Recall, on December 8, the Ethereum network was heldHarfork Istanbul. Its goal was to ensure Ethereum compatibility with Zcash cryptocurrency, increase the scalability of solutions based on zero-disclosure proof technology (SNARKs and STARKs), change the cost of gas of various operating codes (opcodes) in order to complicate spam blocks and increase the network's resistance to DoS attacks.