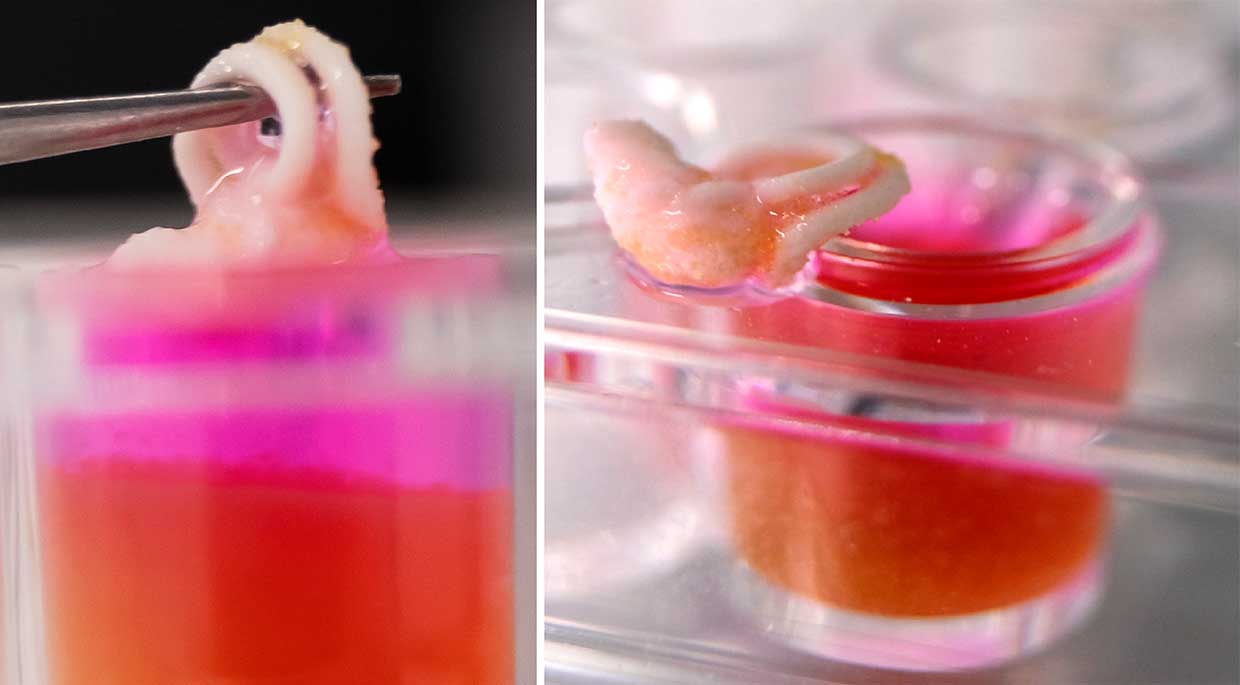
Researchers have developed a ceramic 3D printer ink that allows bone-like material to be printed at room temperature using living cells.
3D printing of internal organs, skin and blood vesselsblood vessels is a difficult task, since all these tissues are composed of living cells. However, bone is a mixture of living and inorganic compounds in a structured mineral matrix. Therefore, printing artificial bones opens up a lot of applications in medicine: from restoring damaged areas totreating cancer and other diseases.
Currently the most progressive methodrecovery is the creation of an autologous graft obtained by harvesting bone from another part of the patient's body. Unfortunately, this method is associated with a high risk of infection and is not suitable if a large amount of material is required.
Therefore, the team of bioengineers from the UniversityNew South Wales has developed a biocompatible 3D printer ink that can be printed in an aquatic environment such as the body. When placed in a gelatin bath or other solution of calcium-phosphate material forms a paste, which at room temperature solidifies into a porous nanocrystalline matrix with a structure similar to bone tissue.
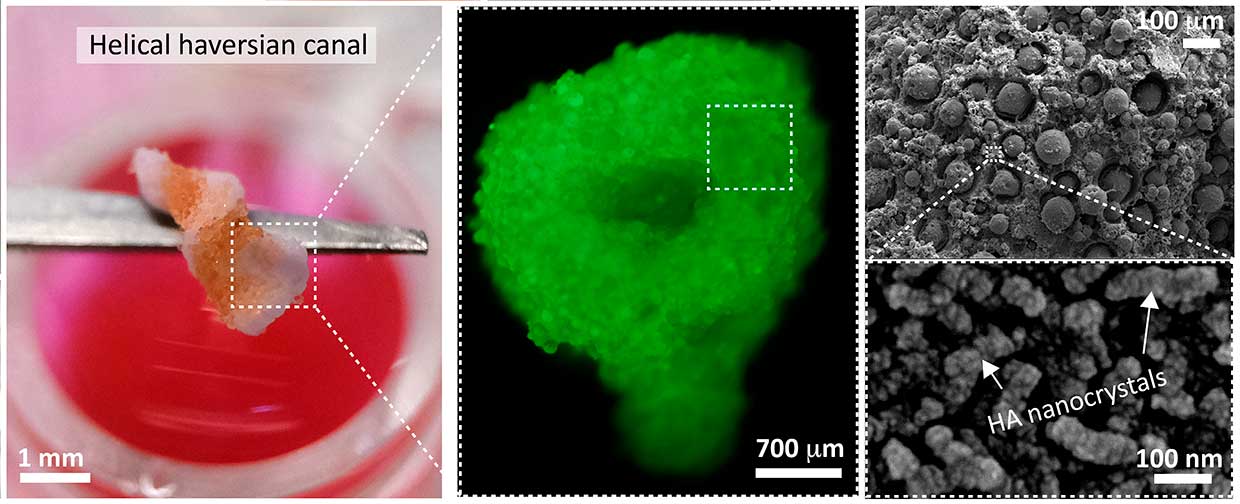
The created ink is suitable for standard3D printers with a special nozzle in the form of a needle with a diameter of 0.2-0.8 mm. In addition to the ceramic composition, they also contain living cells that interact with the artificial structure and divide within a few weeks after printing with 95% viability.
During the study, scientists have successfully createdsynthetic bone structures up to 5 mm in size. The team will then print larger samples and begin testing autologous grafts in small laboratory animals. Ultimately, the technology will allow bones to be printed directly into the patient's body.
Let us recall that earlier scientists also invented bioink and robotic tools for three-dimensional printing of organs directly inside the human body through small incisions.
</p>