A universal framework for understanding incentive systems in cryptocurrency and fiat networks - part 1.
Chapter 0:Moloch
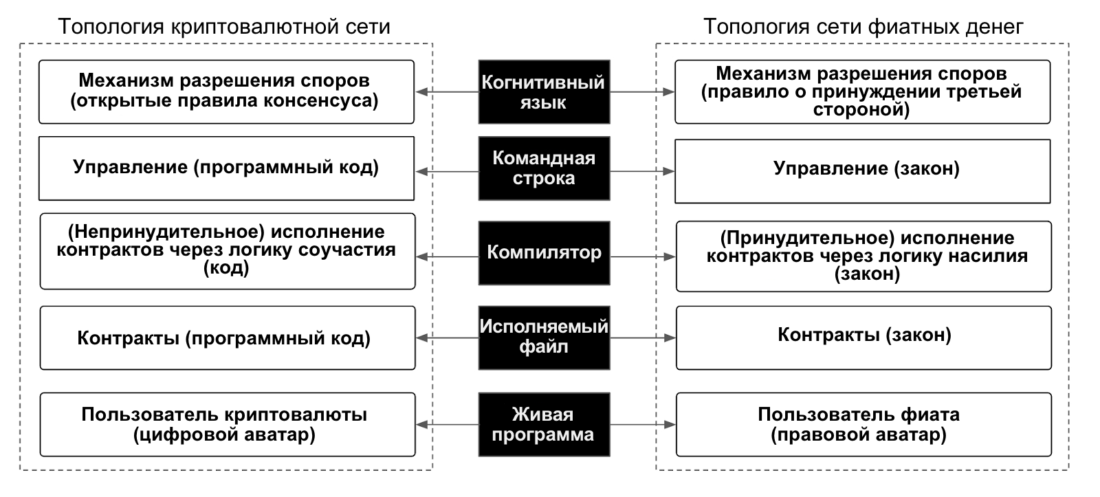
Figure 0: Nakamoto Concept Concept
0.1 What is Moloch?
«Imagine such a dystopiana state in which there are two laws: first, everyone must torture themselves with electric shocks for eight hours a day. Second, if anyone breaks any of the laws (including this one), or speaks out against them, or refuses to enforce them, then every citizen is obliged to take part in the capture and execution of the violator. Let us suppose that these laws are based on well-established traditions which insist on their universal observance.
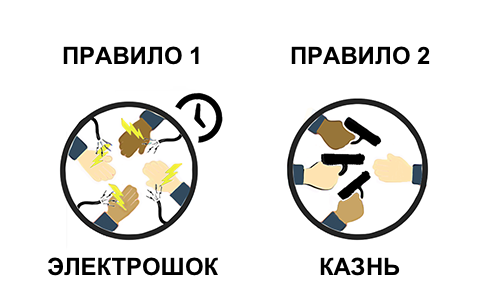
Figure 1: The Rules of Moloch
And you, as a citizen of this state, torture yourself eight hours a day, because you know that otherwise everyone else will be forced to kill you, because otherwisethemselvesdeath awaits, and so on.This order is hateful to every individual citizen, but due to the lack of a good coordination mechanism, it continues to exist. From the point of view of an external observer, we can optimize the system to the state of “everyone agrees to stop doing this at the same time,” but no one inside the system is able to make this transition without huge risk to their own lives.
This example, although somewhat far-fetched,can easily be transferred to a prisoner's dilemma, played out between two participants who again and again come to mutual betrayal. They could achieve a much better outcome if they managed to coordinate, but coordination isit is difficult. From the point of view of an external observer, it is obviousthat two-way cooperation here leads to a better result than mutual betrayal, but no one prisoner within the system is able to achieve this outcome alone.»
– S. Alexander, «Reflections on Moloch«, 2014.
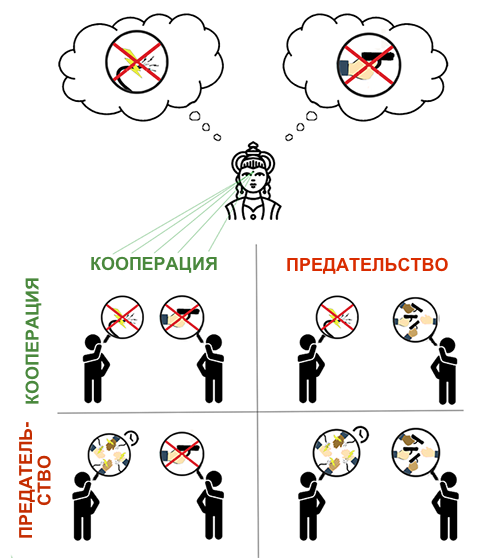
Figure 2: Moloch's rules carried over to the prisoner's dilemma
Bitcoin, through a working softwaretechnology, successfully demonstrated the concept of decentralized distribution networks with minimized need for trust. Thus, he opened the way for a growing ecosystem of retail chains with new configurations. There is a hypothesis that the combination of control based on blockchain and contract technology is a solution that provides the possibility of cooperation between users for many designs of open retail chains.
Prisoner dilemma concept often usedfor modeling economic trade structures and related incentive systems in the framework of game theory. Previously, the confidence necessary to create conditions for trade between strangers was ensured through mechanisms (a) reputation and (b) coercion by a third party, formed due to existing restrictions on the geometry of coordination costs. The emergence of the third category of solutions implies a fundamental change in the supply and demand equation for the creation and functioning of global trading networks and currency systems.
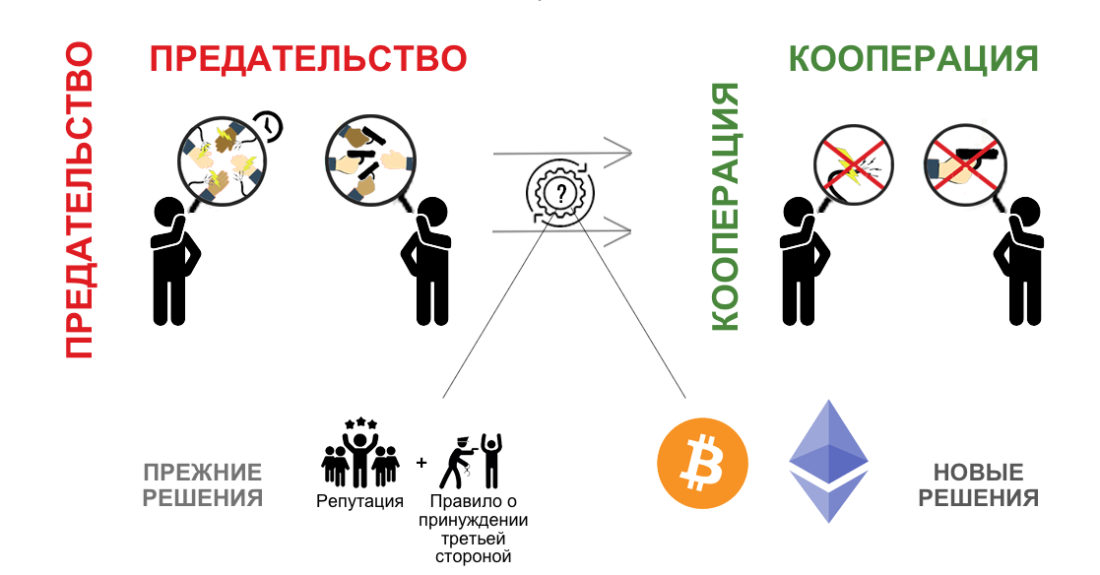
Figure 3: Various solutions for trading between strangers
0.2 Why Moloch wins
Figure 4: Various mental attitudes leading to the birth of Moloch (source)
It has not escaped our attention thatThe system design of the prevailing national network model relies on the use of a custodial bank credit scheme that is globally coordinated and unipolar. This custodial system of bank credit appears to network users as money in the form of bank deposits and physical banknotes. Trading network contracts, including financial instruments, rely on the supply and demand equation for these bank loans to (a) approximate units of value and (b) establish relative price signals for goods and services. On the other hand, this custodial system of bank credit can be thought of and explored as a highly optimized, rent-seeking, co-evolving Moloch memeplex called «fiat». This fiat memeplex encourages netizens to adhere to Schelling's point corresponding to cognitive language:
- geometry of a third-party enforcement rule;
- economic and social mechanisms with a zero amount.
Fiat money incentive structure allowsthe system can reproduce itself despite the fact that its design is bad for users. The reason for this is the cost of coordination needed to change the system. Thus, the transition to a new category of solutions is a socially scalable coordination problem of overcoming the incentive system of the prevailing Moloch.
So coordination costs includethe logical economic primitive underlying the concept of the prisoner's dilemma. The cost of coordination required to achieve the goal depends on the incentive system. The solution implemented in Bitcoin has reduced the cost of coordination by several orders of magnitude. As a result, the cost of decentralization (or states of mutual cooperation and open source consensus) can now be much less than the cost of centralization (or states of mutual betrayal and the rule of coercion by a third party).
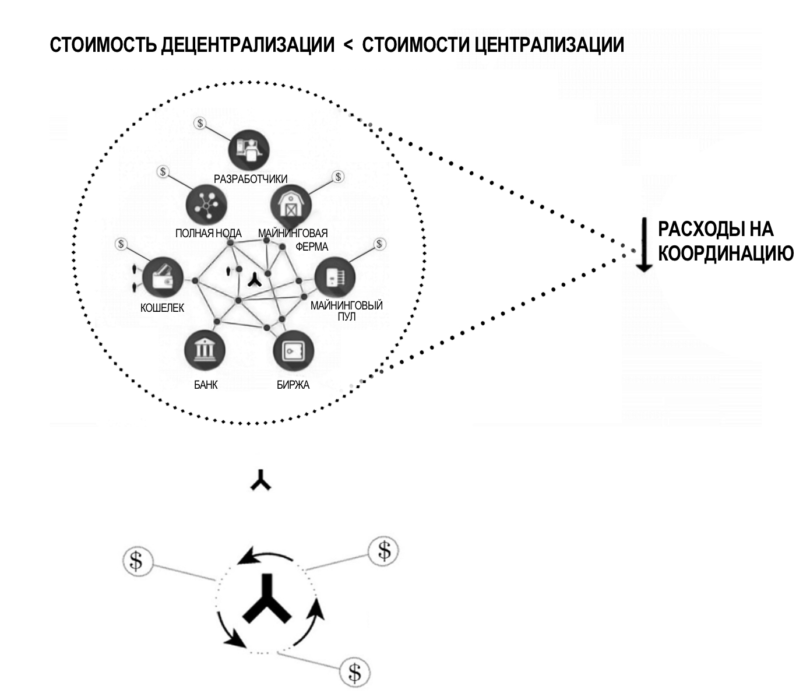
Figure 5: Coordination Costs
User-created system optionsIncentives that are socially scalable for trade and cooperation can now be applied at relatively low cost in competitive and confrontational environments. This can be achieved without having to rely on the geometry of the third-party enforcement rule to successfully replicate the solution. In addition, unlike Moloch’s systems, the cognitive language of mutual respect and open-architecture / open-source systems corresponds to the geometry of a non-zero economy and its associated social mechanisms.
Chapter 1: The Problem of Coordination
1.1 Situation of a non-zero sum
Note: With the exception of graphs and charts, this section is entirely attributable to Robert Wright: R. Wright, “NonZero: The Logic of HumanDestiny. " Vintage Books, 2001.
It is important to note here that:
«Non-zero-sum relationships do not necessarily imply cooperation. This only means that if cooperation takes place, both sides will benefit from it.
We will again look at the prisoner's dilemma with the interrogation of two players.

Figure 6: Prisoner Dilemma Concept
Mutual cooperation is the perfect solution,leading to profit with a non-zero amount. It is in the interest of each player not to betray the other. However, there are two obstacles that prevent them from following such a strategy, which leads to a situation of mutual betrayal. Together, the following two logical primitives can be described as a coordination problem:
- Lack of communication
- Lack of trust
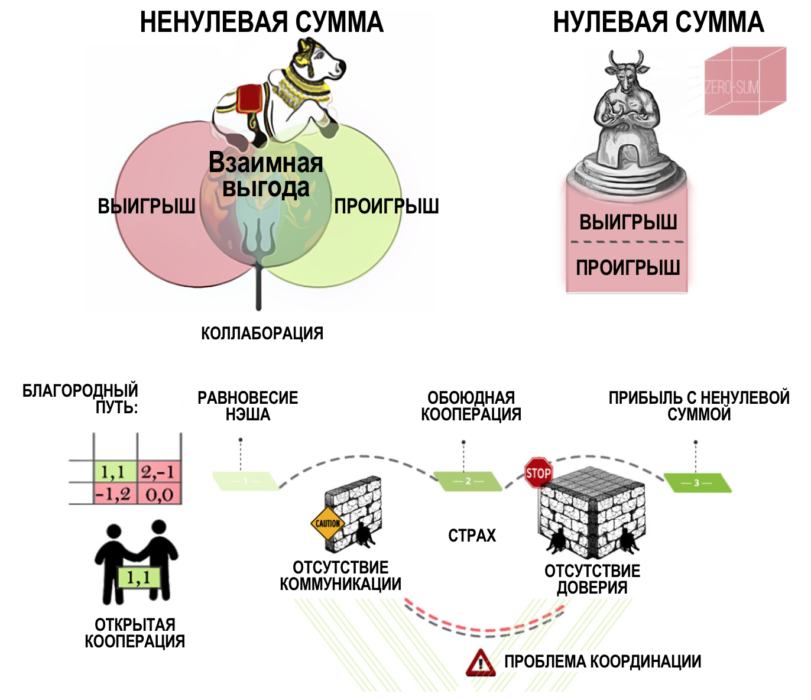
Figure 7: Visualization of a Nonzero Sum Situation
Players cannot agree on a jointstrategies if they are separated by a wall, because of which they cannot communicate. And even if this first barrier, a blank wall, is destroyed, there will still be a fear that the other participant intends to deceive you, and therefore you better betray him first. That is, in addition to the obstacle to communication, it is also necessary to eliminate this fear of being deceived.
1.2 Moloch modern money
Network-level barriers encourageusers adhere to the Shelling point, corresponding to the geometry of the third-party enforcement rule. This makes it possible to create layers of centralized management that provide trustworthy solutions, which are often prone to abuse and manipulation in the mercenary interests.
Lack of channels for transmitting information andestablishing trust between strangers creates the conditions for preserving and reproducing the rule on coercion by a third party - the notorious Leviathan Hobbes - at all levels of the national network. The cognitive language of the third-party enforcement rule allows control layers to more and more efficiently push network updates at the levels of user knowledge, behavior, and contract.
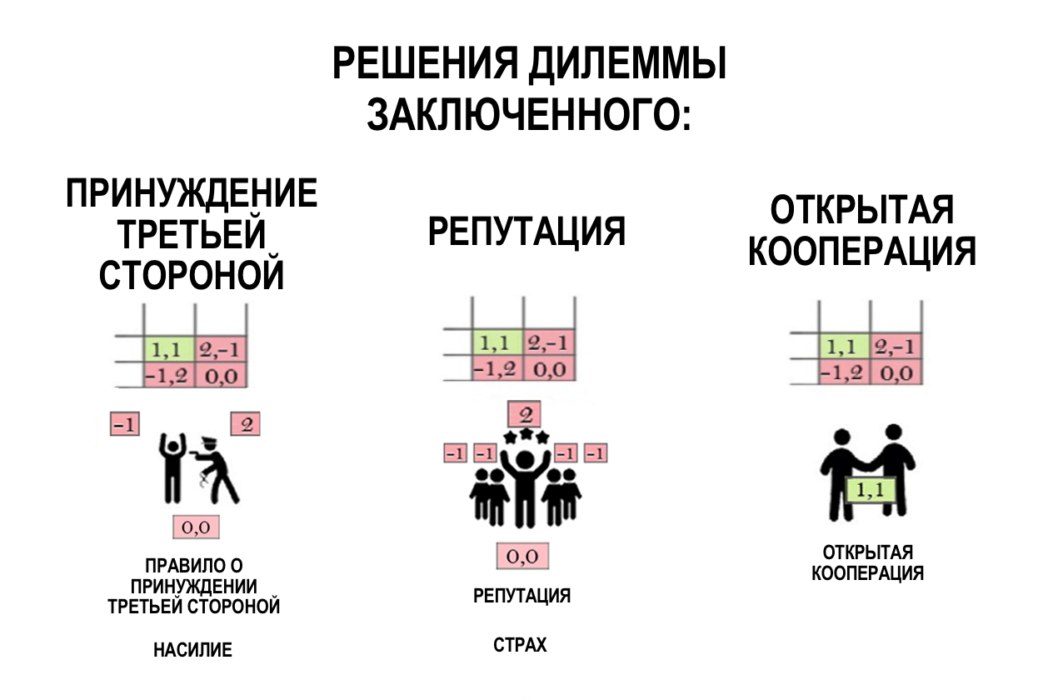
Figure 8: Possible Solutions to the Prisoner Dilemma
For example, existing management based onThird Party Coercion (TPC) has carried out a forced update (PIC) of the global currency network called Fiat, behind which lies a debt-based incentive system (DBS), which implies mutual refusal of users to cooperate.
PTS + POS + DSS = hidden architecture of the situation with zero sum at the level of a distributed system of incentives for the national network.Abstract Moloch takes on flesh.
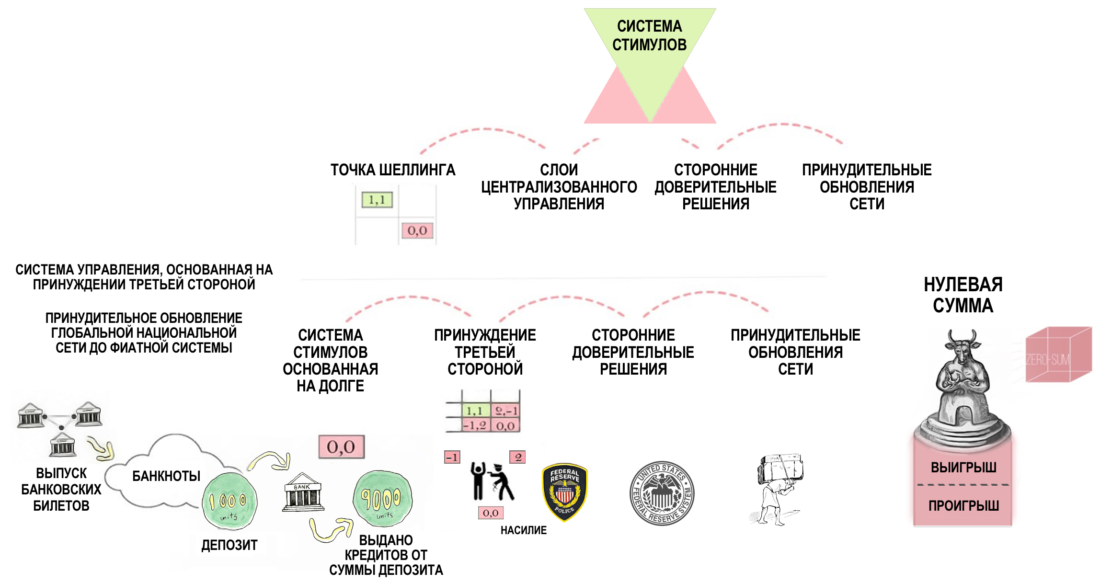
Figure 9: Fiat model as Moloch emerging from a combination of TCP + PIC + LSS
The advent of information technology, with theirfocus on personal freedom, opened up new prospects for the formation of situations with a non-zero amount. Although this solved the problem of communication, the lack of trust was still an obstacle - until Bitcoin was created as a working software technology in the material world. Cryptographic solutions can become the basis for systems and distribution networks that can minimize the need for trust, even in competitive environments with dubious communication.
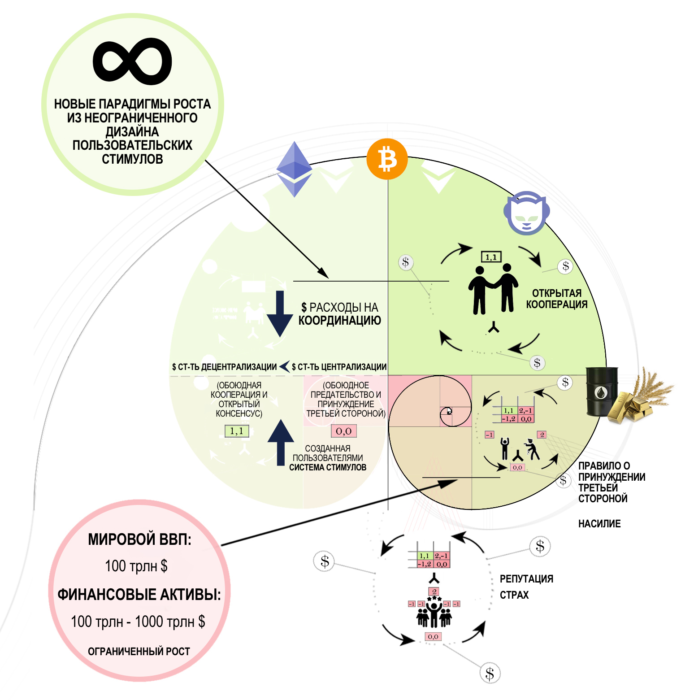
Figure 10: Economic Trade Structures Built on Prisoner Dilemma Solutions
Open Source Consensus Rules +user-centric incentive system without the possibility of forced network updates, can allow network users to solve the coordination problem and build mutual cooperation for profit with a non-zero amount even though each user will act on the basis of personal incentives.
But in order to change the existing system,you must first understand this system itself and the fact that it tends to resist change. In order to solve the coordination problem, you must first clearly understand (a) how existing systems based on the rule of coercion by a third party provide confidence and (b) how Bitcoin with its decentralized management system can provide users with a clear advantage at the level of the incentive system in comparison with fiat.
What do we find useful in the existingviksawaakye– is a universal framework that can bring clarity and help sharpen our methods to enable this transition and successfully create a decentralized economy.
We'll start by shedding light on the conceptmoney and briefly trace its evolution in terms of the design of the incentive system. Then we will introduce the Nakamoto conceptual framework and use it to indicate the intersections between the fiat and cryptocurrency systems.
Chapter 2: What is money?
Common definitions of money - such as a meanspreservation of value, medium of exchange or unit of account - are formulated from the point of view of their use. It is extremely rare to find the definition of money given in terms of their existential nature. Money is an energy deal. At the system level, money is a variant of the incentive system. More specifically, money is a distributed system with a built-in incentive mechanism.
The evolution of money can be divided into three stages.
Stage I
The canonical story begins with barter systems in which people exchanged some goods for others. This can be considered as a distributed mesh network with an upstream model, as in the figure below.
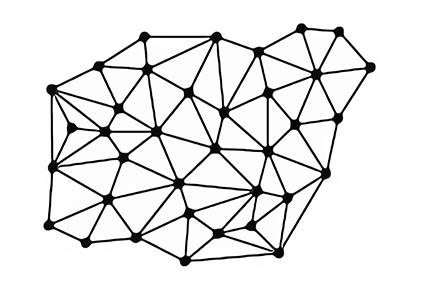
Figure 11: Barter system represented as a mesh network
Each user can exchange ortrade goods with any other user in barter trading pairs. However, shortcomings of this system (double coincidence of desires, complexity of cost transfer, lack of social scalability) became apparent, as a result of which institutional entities began to attempt to improve the design of this system.
Stage II
In other words, commodity flows in various commodity trading pairs of the barter network began to be redistributed in favor of more efficient trading geometries.
The network of trading pairs has become more like a wheelwith spokes apart from the sleeve, rather than a wire mesh. The pressure of selection and the limitations of social scalability lead to the emergence of multicenter supernets on the network. These super nodes began to offer common trading pairs, to which users often resorted to trade other goods. As of now, there are quite a few direct markets for unique altcoin trading pairs. Instead, most altcoins first go through the more common trading pairs with BTC or ETH. This design can be considered as a multicenter distributed network, as in the figure below.
Figure 12: Monetary system represented as a multicenter distributed network
Super nodes covering the most frequently tradedbarter couples selectively became interested in the adoption of certain information technologies, such as metals, stones, grains, mollusks and beads, as their own incentive to trade in other goods - perhaps for ideological reasons or because where these supernatives imported from goods, beads, shellfish or gold were preferred barter pairs, or because the laws of electrostatics made metals (such as gold) easily verifiable. As breeding pressure increased, technologies — such as jewelry and collectibles, metals and beads, shellfish and legumes — sought to create new incentive systems for trading in various barter or commodity pairs. Thus the technology of money appeared.
Stage III
According to the canonical version, the technology of money solved the problem of barter inefficiency, or the need for a double match of specific trading pairs.
However, as global growth continues,trading networks, settlement operations, transportation and storage of money (whether it be jewelry and collectibles, metals and beads, shellfish and legumes) posed new challenges to the monetary system. This scaling problem was solved by creating a currency. The currency, in essence, was a receipt confirming ownership of the monetary units used in a particular network. A good example of this approach from recent history is the era of the gold standard. During the gold standard, on every banknote issued by the American government, it was written:
«This confirms that X dollars in gold coins have been deposited in the treasury of the United States of America, payable on demand to the bearer of this note».

Figure 13: Twenty-dollar receipt for the right to receive the appropriate amount of gold from the bank
This means that the state provided safe storage of money in a financial institution, and the currency was used as receipts giving the right to receive this money.
This was a form of custodial decision in whichthe state and banks were responsible for storing network tokens (money) and issued a kind of receipt (currency) with the right to demand network tokens so that users could exchange these receipts for goods and services.
Most of the accounting and balance sheet transactions were carried out in foreign currency, that is, at the level of token ownership receipts, with periodic settlement at the network token level.
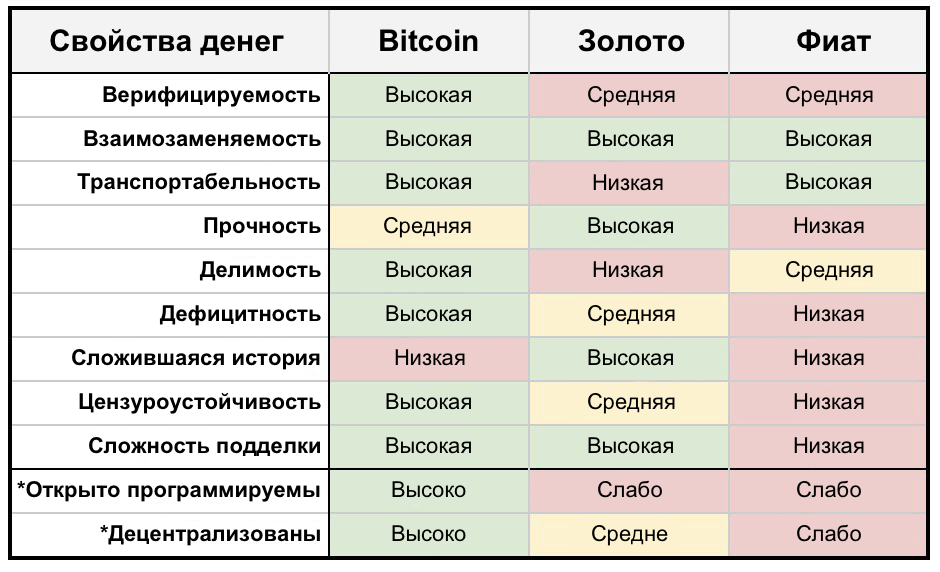
Figure 14: Comparison of Bitcoin, Gold and Fiat Money. (a source)
Chapter 3: Force Network Upgrade
In the canonical version, the modern era,which replaced the gold standard, is often presented as «scientifically innovative» a consensus understanding that emerged in the 1960s and 70s that allowed the modern world economy to scale after World War II and avoid another Great Depression.
In fact, to the global economic networka forced update was applied, namely, the choice in favor of a fiat currency incentive system that erases the differences between real money and currency.
«Before the First World War, the banking systemThe US (and most of the world) was based on gold, and despite periodic government intervention, banks remained free rather than controlled. From time to time, as a result of the overdevelopment of the credit system, banks were forced to reduce lending to the level of their gold reserves. In these cases, interest rates skyrocketed, no new loans were made, and the economy entered a short but turbulent period of recession. It was the limited gold reserves that stopped the unbalanced expansion of business before it turned into a disaster like the one that happened after the First World War. The periods of economic reorganization were short: it quickly recovered and continued to develop on a renewed, healthy basis.
However, the healing process was mistakenly taken fordisease. If shrinking bank reserves leads to lower business activity, advocates of government intervention argue, then why not invent a way to help banks increase the amount of reserves they have, so that cutting them is out of the question? It was stated that if banks can issue loans in any volume, then businesses will not have to face the problem of an economic downturn. Thus, in 1913, the Federal Reserve System was created. It included 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, which were only nominally owned by private individuals, but in reality, financing, support and control over them were entirely exercised by the state. Loans issued by these banks were, in practice (although not a word was said in the law about this), reimbursed by the federal government through tax revenues. Formally, we remained within the gold standard: individuals could still freely own gold, and it was also used as a bank reserve. However, now, in addition to gold, loans from the Federal Reserve Banks ("paper" reserves) became another legal means of paying deposit holders.»
– Alan Greenspan (Ayn Rand, Nathaniel Branden, Alan Greenspan, Robert Hesse, «Capitalism. Unfamiliar ideal«, 1967)
In the decades since forcednetwork updates with the transition from the gold standard to fiat, the currency ceased to fulfill the function of a receipt with the right to demand the underlying money, or tokens of the financial network, and began to exist exclusively as a bank loan. A bank credit currency standard was introduced for each network user through the geometry of a centralized third-party enforcement rule underlying the management models used in fiat networks. The combination of policies, existing institutionalization, and laws on centralized means of payment ultimately led to the formation of a system that looks something like this:
Figure 15: Fiat system as a monocentric network
This system design has been accepted by all countries.of the world, and the network of each country imposes its bank credit tokens on users. These requirements for bank loan tokens are euphemistically called national, or sovereign, loans. Existing regulatory frameworks provide protocols and sets of rules governing the movement and functioning of these requirements for bank credit tokens in a trading network. For example, a USD token request acts as a network token to initiate a read / write operation within a bank denominated bank credit storage system denominated in dollars.
«Every time you receive anyof fiat currencies, you issue a loan - you provide a product or service to a third party in exchange for a banknote, this is a loan. You are showing trust. Your full trust and loan is based on completely irrational thinking, unless «full trust and credit» are not part of your belief system»,
– Andreas Antonopoulos, «Money internet«, 2016.
«Когда вы или я выписываем чек, на нашем There must be enough funds in the account to pay that amount, but when the check is written by the Federal Reserve [or the bank makes a loan], there is no bank deposit on which the check will be written. When the Federal Reserve writes a check [or a bank makes a loan], it is the act of creating new money»,
–Boston Federal Reserve Bank (F. R. B. of Boston, “Putting it Simply - the Federal Reserve”. Public Services Department, Federal Reserve Bank of Boston, 1984.)
It was the official global networkparadigm until in 2009 Bitcoin was proposed, which over the years has become a working software technology. This has led to the creation of new, user-oriented and practical utility options for incentive systems.
We can compare these incentive systems by studying the basic topology of fiat and cryptocurrency networks. For this, we will use the Nakamoto conceptual framework.
Chapter 4: Nakamoto Conceptual Design
At a high level of abstraction, the life cycle of computer programs can be divided into the following five layers.
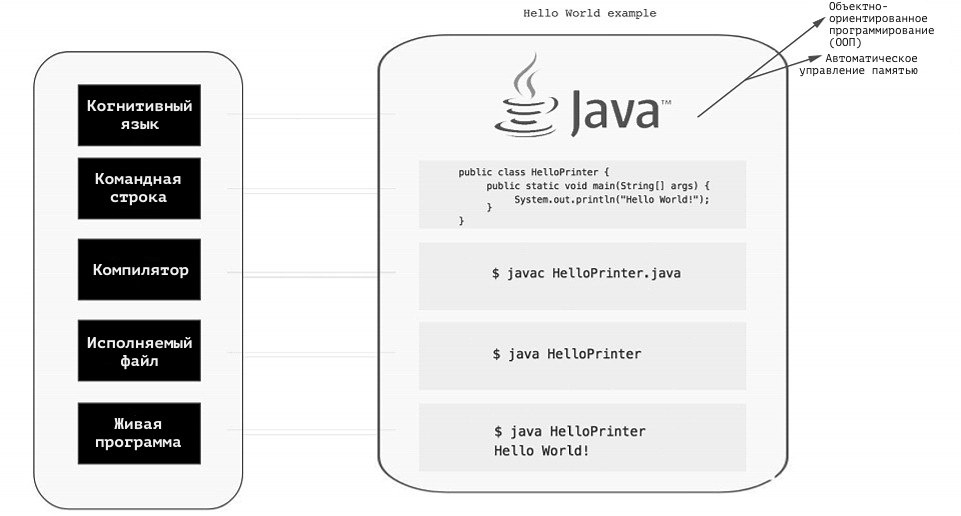
Figure 16: Computer program life cycle in Java syntax
- The live program layer consists of users using this system software.
- The executable file is used to access the system software.
- The compiler is used to create an executable file.
- The command line is used to issue commands, such as compiling code and deploying an executable file or updating system software.
- The layer of cognitive language describes the mental settings of the author of the program code, as well as the manifestation of these mental settings in the developer's environment and system software.
Therefore, we offer a conceptual schemeNakamoto as a universal framework for understanding the connections that exist inside and between cryptocurrency and fiat networks, inspired by the fundamental principles of computer science.
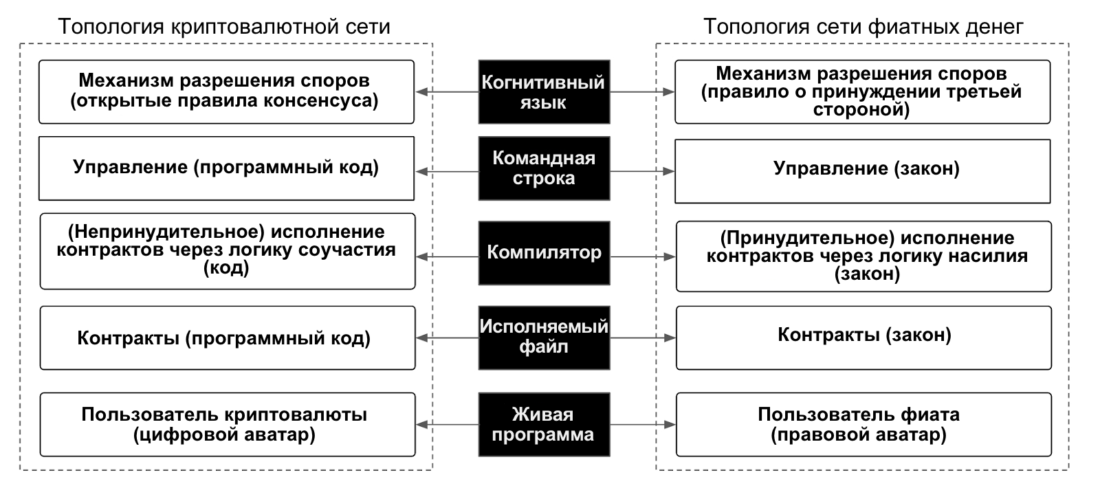
Figure 17: Nakamoto Conceptual Diagram
Nakamoto's scheme can be used not only fordisplay and understand the fundamental differences between the topologies of fiat and cryptocurrency networks, but also to study the different layers or subsystems of each of these networks at the code and incentive levels to identify hidden Schelling points caused by a third-party coercion rule, and then refactor and optimize this layer or the whole system to increase resistance to attack vectors.
For our current goals, using the Nakamoto scheme will allow us to:
- Compare the design of fiat and cryptocurrency networks at the system level by comparing one-to-one reduced logical primitives.
- Clearly understand the benefits of a decentralized economy and what aspects need to be decentralized to create such an economy.
- With clear thinking, approach the problem of scaling and learn how to achieve the goals of scaling without affecting the decentralization or network resistance to attack vectors.
- Solve the problem of scaling on the contract layer and create more competitive and open retail chains.
- Refactor existing andof the proposed code of a centralized and decentralized exchange in order to include a distributed incentive system in it, as well as to identify and eliminate the hidden Schelling points caused by the third-party coercion rule.
In the second part of this series of articles we will continuestudying the conceptual scheme of Nakamoto and using it we denote the existing intersections between the fiat and cryptocurrency systems. We then use these findings to solve some of the problems of the financial industry. Finally, we will examine the current state of art and how we can improve the design of incentives for existing cryptocurrency systems in order to facilitate the onset of the desired changes. Only then can we begin to reorganize the subsystems of these decentralized frameworks, improving scaling without compromising decentralization or the network's resistance to attack vectors.
</p>