A bitcoin mempool is a place where transactions are waiting to be picked upminers to add to the block on theblockchain.
If you've ever made a BTC transaction, you've experienced the fact that from time to timedispatch to receipt is up to 10 minutes.network congestion, it could be hours, and sometimes days.You may have also heard the phrase "Transaction stuck in mempool".This is exactly where data is stored waiting to be processed by nodes.In the Bitcoin network, data is transactions, so a mempool can also be called a transaction pool.
If the size of the mempool increases, this means that there are more transactions in the queue. Confirmation will take more time, and to speed up the transaction you will have to pay a fee.
Mempool is part of BIP 35. The idea was that external nodes would be able to access memos of other nodes. This is important for the following:
- Bitcoin wallets can find out about the speed of transactions before sending (divide the mempool size by block size = how many blocks should be expected for about 10 minutes each),
- miners can prioritize transaction processing by fees,
- the observer can diagnose the network.
How does bitcoin mempool work?
Let's say you decide to send yourbitcoins. You do this by executing a transaction. To conduct it, you must specify the number of bitcoins that you want to send, the wallet of the addressee to whom the transfer should be made. Confirming that you are making a transaction, the wallet will be redirected to the following actions:

- Sign the transaction with secret keys
- select one of your unspent transaction outputs necessary for its construction;
- will transmit the transaction to the Bitcoin network and prepare it for full verification.
This is where mempool comes into play. Your transaction will not be completed at the time of its transmission. Instead, it will be saved in mempool. It is called that because the nodes store it in their RAM memory.
Node -It is an electronic device that is part of the network.At the same time, each node contains a complete copy of the blockchain.The number of these nodes around the world varies greatly from time to time.time due to many reasons, most of which are related to the cost of maintaining the health of the node and the volume of Bitcoin Core.

For your transaction to complete, you need to confirm / verify it. To start this process, at least one miner must pick it up from the mempool and check it.
MinersAre people who use their computersto process and confirm transactions. The more times one transaction is confirmed, the less likely it will be compromised. Ideally, a transaction from a mempool will be verified 6 times before it becomes part of the blockchain.
Transaction Confirmation -This is a task that requires a lot of computing power and electricity, so every time a minerverifies the transaction, he is compensated for his efforts in Bitcoin.This fee is presented in satoshis (1 satoshi = 0.00000001 BTC) for each transaction file and is usually set by the transactionator.Not all transactions have the same transaction fees, so miners canlook at the mempool and choose which transactions they want to verify.Obviously, most of them will be motivated by financial gain, so a trade with a higher fee is likely to beundertaken and approved by the miner.
Once your transaction has been verified,it will become part of the next block - a set of unique bitcoin transactions that have been verified. As soon as one block is filled with confirmed transactions, it will be added to the blockchain and confirm all the blocks preceding it. After adding this block to the blockchain, all transactions that became part of it will be deleted from their respective modules. This will reduce the size of the mempool and create space for information about new unconfirmed transactions.
The main problem faced by mempool– its size, which varies depending on the number of nodes, as well asCurrently, a single blockchain block is limited to a size of 1 MB.In addition, there are limits to how long it will take to mine a new block - it isAll these measures are necessary to create a bottleneck in the network, which is the regulatory mechanism for bitcoin trading.They stop block overflows and ensure that Bitcoin's value doesn't drop.
The problem isis that it can lead to the growth of the mempool.When a certain value is reached, the mempool, in order to avoid overflow, will start to reduce some low-priority (mostly low-cost) transactions.A discarded transaction does not disappear completely; All it takes to become a part of the mempool again is a relay.
Mempool is part of a Bitcoin development document called BIP 35.It is used as a standard method of conveying ideas to improve technology.These documents are very important for development, as bitcoin does not haveThe mempool allowed for increased transparency and better control over unconfirmed transactions.It also entailed the creation of lightweight SPV wallets that don't requiredevices to store all the data of the blockchain, which allowed mobile phones and other devices with limited space to become part of the Bitcoin network.
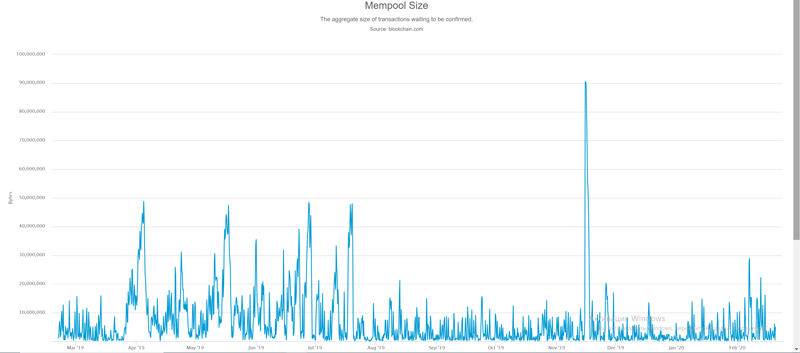
Where can I see the size of the mempool?
Although blockchain and mempool are related to each other, butthe mempool itself is not a part of the blockchain. He doesn't have a single place. Rather, each Bitcoin node has its own mempool with memory capacity. Nodes are managed by miners and full node operators who run copies of the blockchain on their devices.
To find out the size of the bitcoin mempool, you need to use the online service https://www.blockchain.com/
5
/
5
(
1
voice
)