The number of new bitcoins created every 10 minutes is halved every four years. Thiscalled halving (from the English. halving - halving). The next halving will be the third for Bitcoin and will happen in May this year. After that, the current block reward of 12.5 BTC, paid every 10 minutes, will be halved to 6.25 BTC. Given that Bitcoin’s total emission is limited to 21 million coins, halving the block reward doubles the time it takes to issue the remaining BTC. But it also means that over time, fewer new bitcoins will be issued, and due to the limited volume of emissions, bitcoin will become increasingly scarce.
And scarcity raises the price.
Historically, Bitcoin halving has been an important catalyst for launching another bull market.
In fact, usually a new upward trend in bitcoin begins at least a year before the halving.
But what effect does halving have on the price of bitcoin?
In this article I will try to answer the following questions:
- How did each of the two previous halvings affect the price of bitcoin?
- Are there any recurring trends in the effect of these two halvings on the price?
- What impact can the upcoming third halving have on the price of bitcoin?
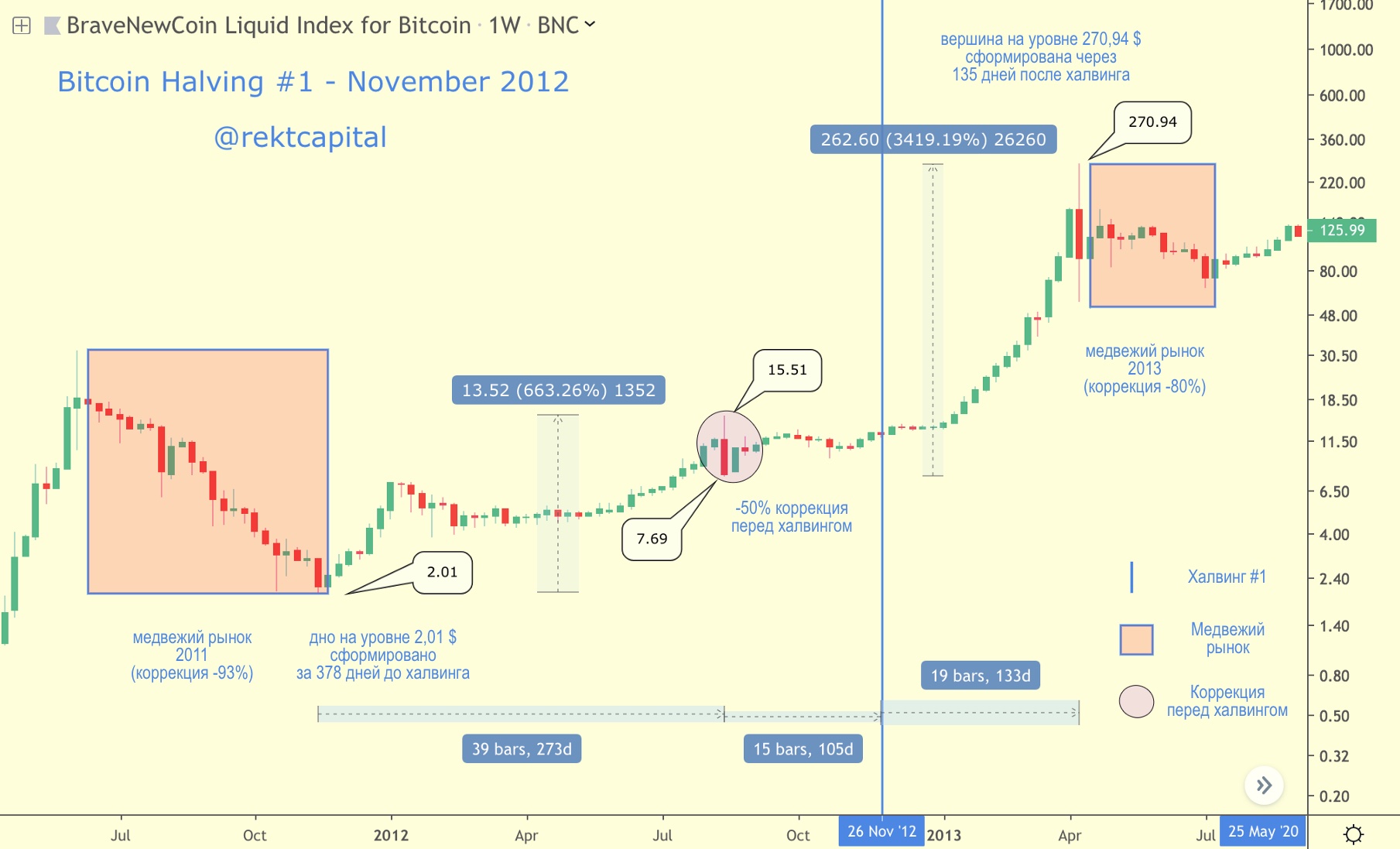
Halving # 1 - November 2012
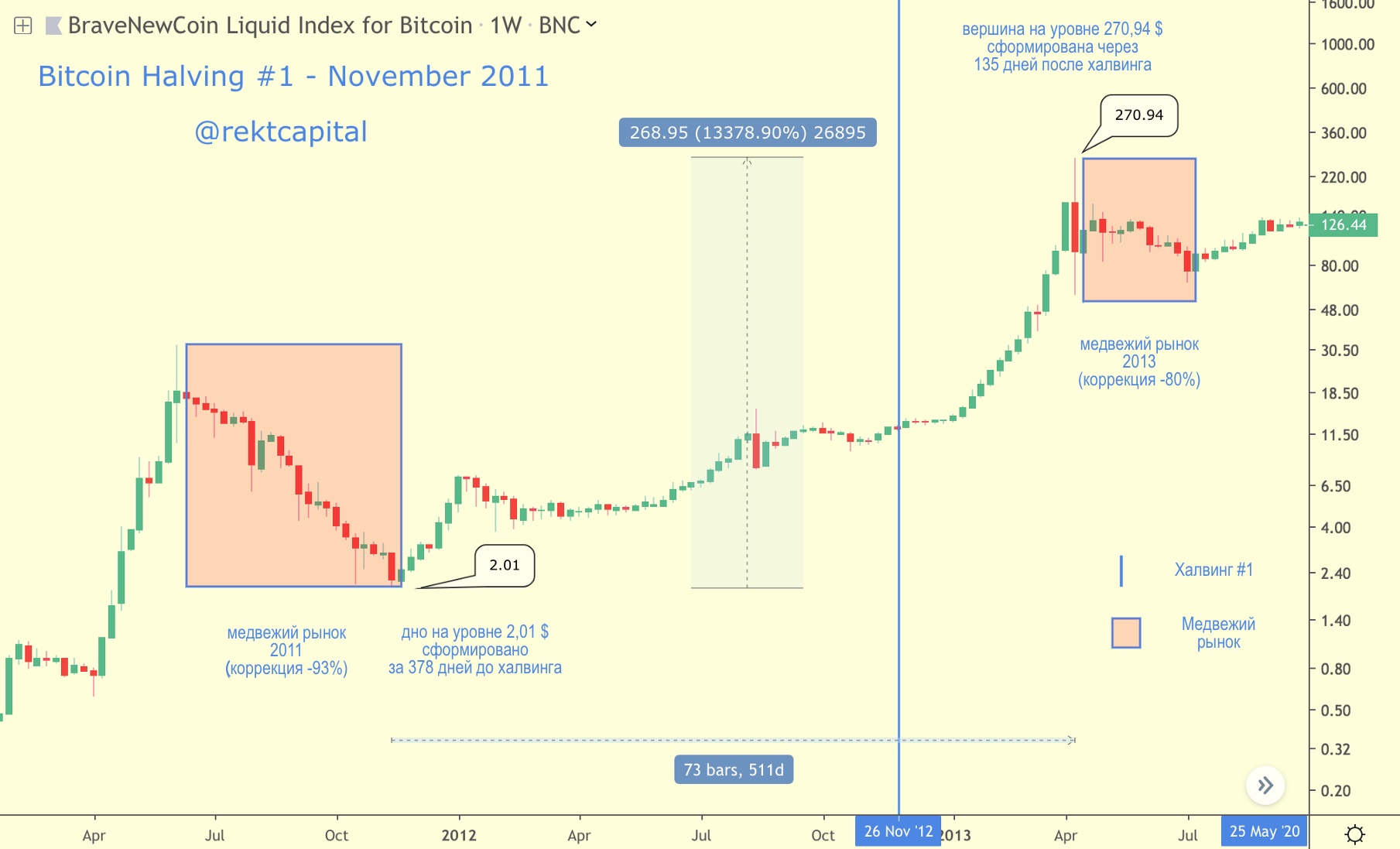
BTC price in the context of the first halving
Bitcoin's first halving took place at the end of November 2012.
Bitcoin rally from $ 2.01 up 13,000% up to the peak of the cycle at $ 270.94, took ~ 513 days.
The first halving was a key catalyst for the new bull market and the significant rise in bitcoin prices.
Upon reaching a peak at $ 270.94, the 2013 bear market began, in which the BTC price fell by 80%. The bear market lasted approximately 87 days.
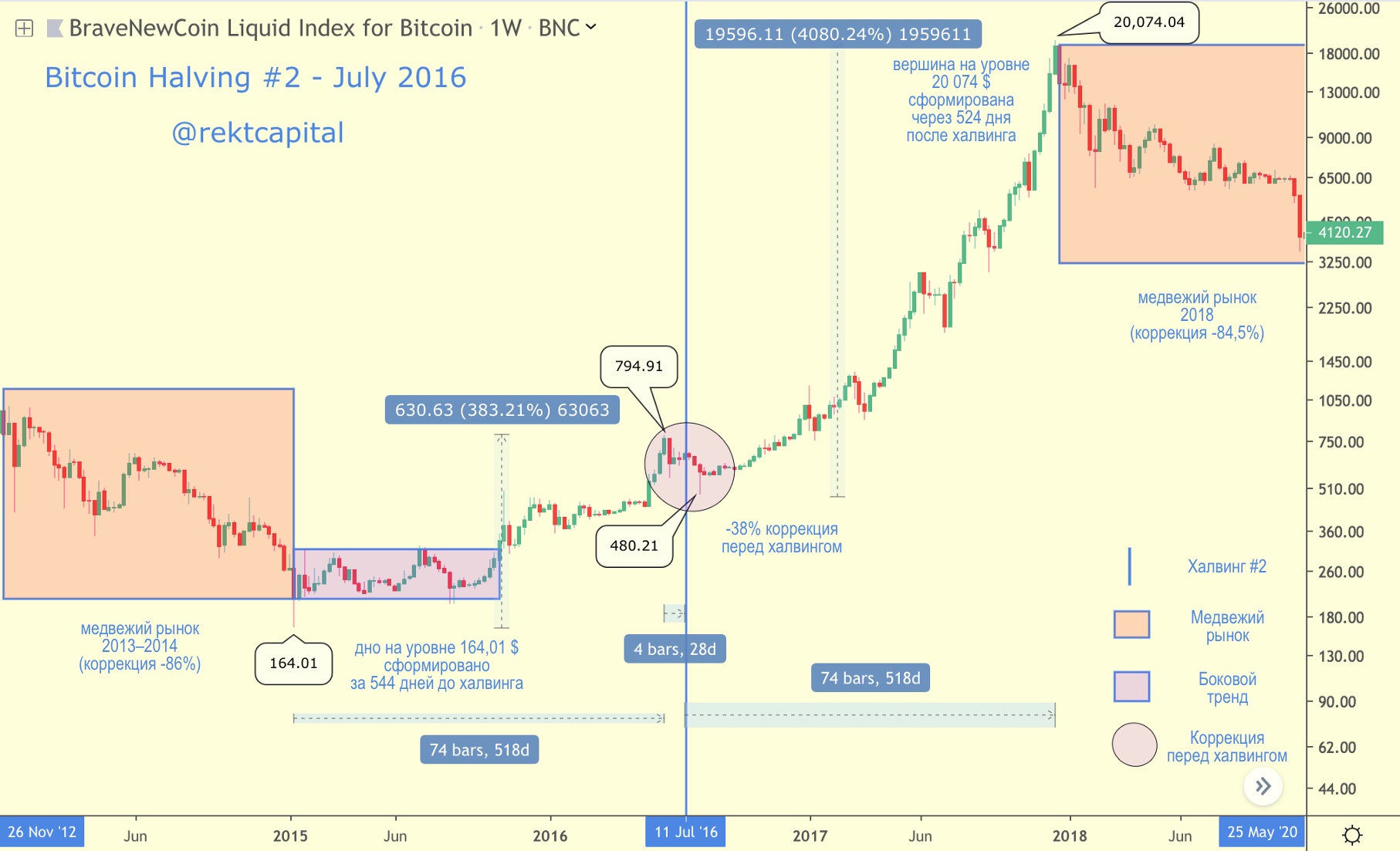
Halving # 2 - July 2016
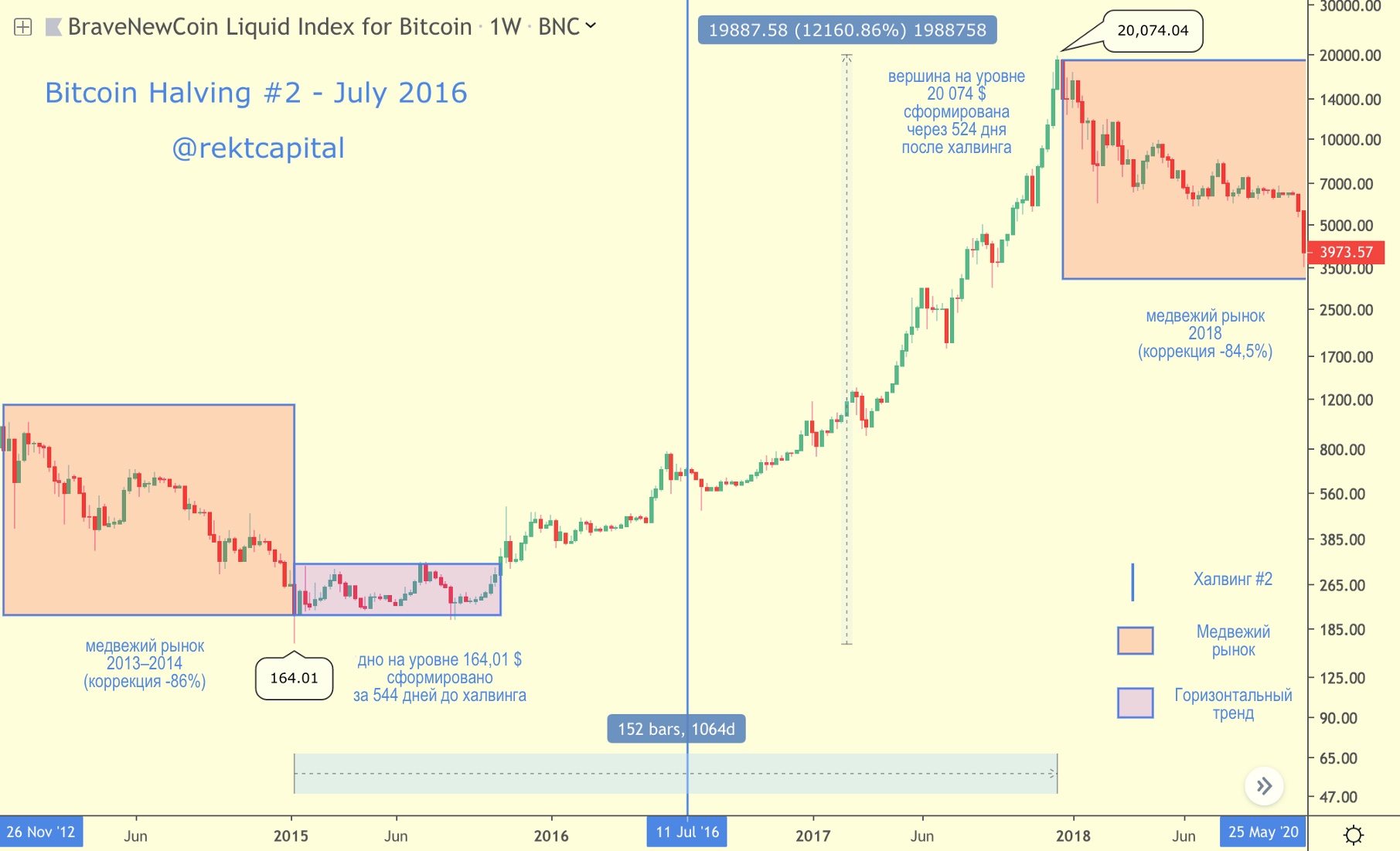
BTC price in the context of the second halving
Bitcoin's second halving took place in early July 2016.
Bitcoin rally from $ 164.01 up 12,000% up to the peak of the cycle at $ 20,074, took ~ 1068 days.
Upon reaching a peak at $ 20,074, Bitcoin entered the 51-week phase of the bear market and hit the bottom in mid-December 2018.
Key findings from a comparison of the first two halvings
1. Halving - the most important catalyst for the start of a new bull market in bitcoin
Historically, halving has been a key catalyst for moving Bitcoin into a new bull market.
Bitcoin price rises both before halving and many months laterafterhim.
In fact, the price of bitcoin set new historical highs as a result of halving.
However, these new price highs took many months to set.afterhalving
2. In each of the previous halving cycles, the BTC price increased by 12000–13000%
In the price rally of both halving cycles, a certain similarity was observed.
Consider first the first halving.
It took 513 days for Bitcoin to grow by 13,304% from $ 2.01 before halving and form a new maximum at $ 270.94 after halving.
Now let's take a look at the second halving cycle.
It took Bitcoin 1068 days to grow by 12,168% from $ 164.01 before halving and form a new maximum at $ 20,074.04 after halving.
The similarity is that from the lower values of the bear market before halving to the peak of the bull market after it, the price of bitcoin in both cases increased by 12000–13000%.
An important difference is that in the second halving cycle this growth took twice as much time (1067 days compared to 513 days at the first halving).
How does this compare with what we already know about the upcoming third bitcoin halving?
Halving # 3 - May 2020
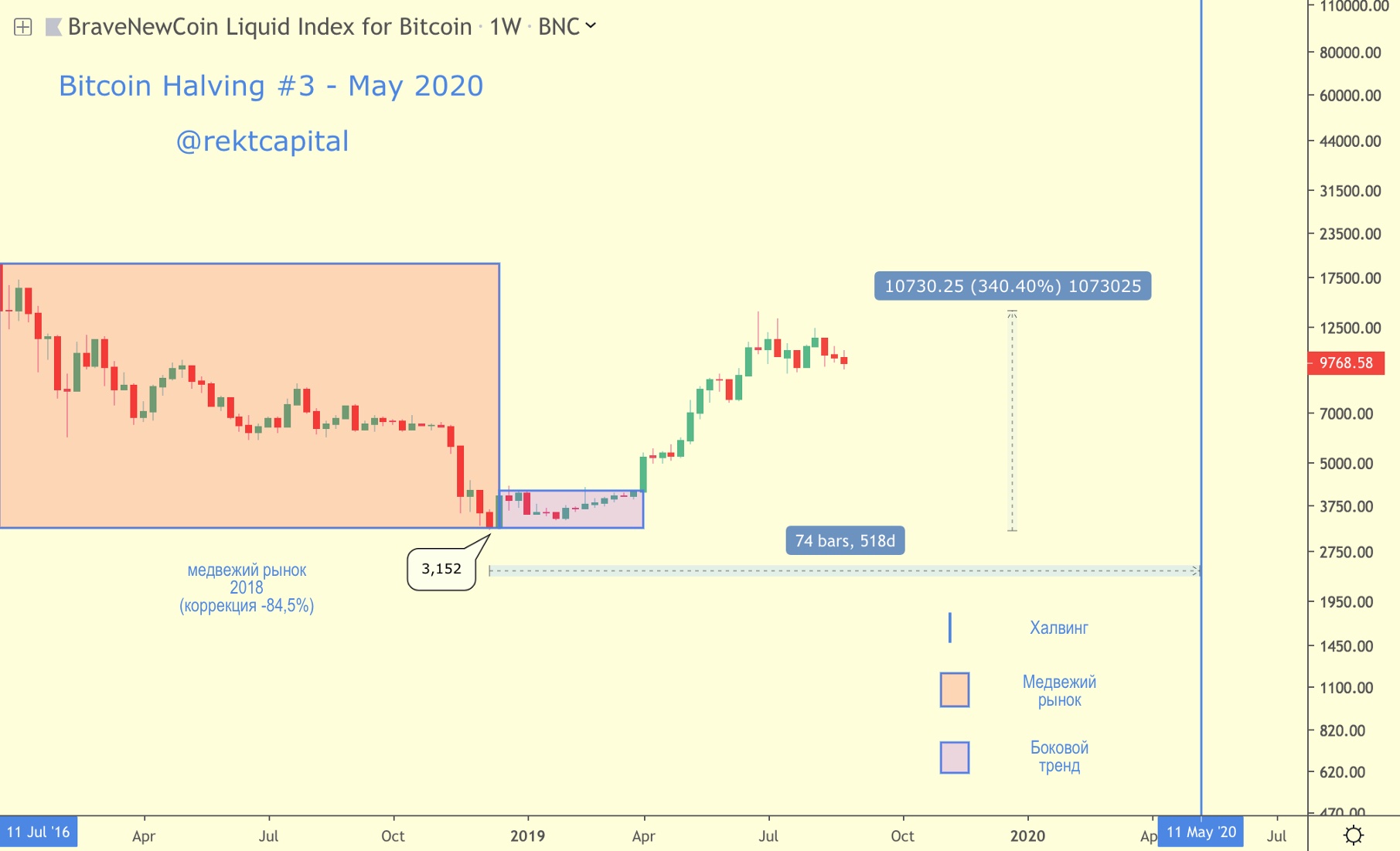
BTC price in the context of the third halving
The expected date of Bitcoin’s third halving is May 17, 2020.
So far, it can be said that it took Bitcoin more than 260 days to grow by more than 340% of the bottom formed in mid-December 2018 at $ 3,152.
This means that lower price values were recorded approximately 519 days before the third halving.
This is interesting because there are some important coincidences with the second halving cycle.
Here are the relevant numbers for the second halving:
- Lower prices for BTC were set 544 days before the second halving.
- The local peak for the BTC price before halving was formed after an increase of 383%.
So far, the price fluctuations of Bitcoin on the eve of the third halving are very similar to the behavior of the price before the second halving.
This is an important cross-cutting topic, so let's take a closer look at the behavior of the BTC price ahead of the halving.
Let's try to divide price movements byperiods before and after halving to identify additional recurring trends or patterns that could contribute to a better understanding of what to expect from the upcoming third halving.
Halving # 1 and # 2 - detailed analysis
Halving # 1: BTC price before and after halving
Halving # 2: BTC price before and after halving
Key Trend # 1
Most of the exponential rise in Bitcoin price associated with the halving occurred duringafterhalving
Ahead of the first halving, Bitcoin rose 663% and set a local «pre-halving» maximum at $15.51.
Having formed the bottom after a 50% correction before halving, in the period after the halving, BTC increased by 3400% and set a new historic maximum at $ 270.94.
Ahead of the second halving, Bitcoin rose 383% and set a local «pre-halving» maximum at $794.91.
Over 524 days, BTC grew by 4080%, forming the top of the market cycle at $ 20,074.
In summary:
- In the first halving cycle, growth after halving was 5 times greater than growth before halving.
- In the second halving cycle, growth in the period after halving was more than 10.5 times higher than growth in the period before halving.
It is clear that most of the exponential rise in Bitcoin price associated with the halving occurred duringafterhalving
It turns out that Bitcoin updated the historical maximum after each of the previous halvings.
Upon reaching a new historic high, Bitcoin is likely to form the top and move into the bear market phase, in which the BTC price will be adjusted by at least 80%.
Key Trend # 2
In the periods before halving, bitcoin experienced a stronger and more rapid growth in the first halving cycle than in the second.
The price rally to a local maximum before the first halving was almost twice as strong (663%) than an increase to a local maximum before the second halving (383%).
In fact, it took half the time of the Bitcoin halving cycle.
In summary:
- In the first halving cycle, Bitcoingrow by 683% and reach a local peak before halving, it took 273 days. In the second halving cycle, a similar rally to the local peak raised the price by 383% and it took 518 days.
Key Trend # 3
If the price of BTC rises less before halving, then growth after halving is greater than in the same period of the previous cycle.
In the first cycle, the price increase to a local peak before halving amounted to 663%, and after halving - 3400%.
In the second cycle, the price increase to a local peak before halving amounted to 383%, and after halving - 4080%.
Key Trend # 4
In both cases, there was a significant recession before the halving – a «shaking out» from the market of weak players.
Many investors fell into the trap of this correction before halving.
Many investors are selling theirbitcoins to take profits, while others dump them out of fear of a strong downward movement, resulting in them being «shaken out» from their positions.
Both of them miss the exponential growth following the local correction.
Even a simple awareness of the presence of suchTrends may help some investors avoid this kind of participation in the current halving cycle, if, of course, the story repeats itself and a similar rollback occurs again.
That is why, for a better understanding of the current situation, it may be useful to analyze and compare these corrections from previous halving cycles in more detail.
First, look at the correction before halving # 1.
Correction before halving # 1:
a) occurred 100 days before the halving,
b) its depth was 50%,
c) lasted only 2 days.
But that was enough to shake outpositions a fair number of investors (despite the fact that by the day of the first halving bitcoin had won back almost all of this briefly lost value).
Having formed the bottom after a 50% correction before halving, in the period after the halving, BTC increased by 3400% and set a new historic maximum at $ 270.94.
Now let's look at the correction before halving # 2.
Five hundred twenty-one days Bitcoin tookin order to grow by 383% from the lower values of the beginning of a new cycle to a local peak before halving at $ 794.91, after which the price moved to correction (it is interesting that it took approximately the same number of days to establish a new historical maximum at $ 20,000 - 524).
This correction before the second halving is quite different from the same phase of the first cycle, because it:
a) occurred 24 days before the second halving,
b) its depth was 38%,
c) lasted 44 days,
g) lasted for 20 days after halving.
A correction time of 44 days implies that it continued after the second halving.
Thus, the price trend at the time of the first halving was upward, and at the time of the second halving - downward.
In summary:
- Correction before the first halving occurred approximately 100 days before the halving, its depth was -50%, and the duration was 2 days.
- Correction before the second halving occurred 24 days before the halving, its depth was -38%, and the duration was 44 days. Correction continued for another 20 days after halving.
Although there are no clear similarities between these correctionsviewed, it is still important to know about their specifics - at least in order to form more reasoned expectations regarding the likely limits of correction in the third halving cycle.
Key Trend # 5
The local peak before correction in the middle of the halving cycle has historically been the highest price point before halving, but not high enough to update the historical maximum.
At the beginning of the next halving cycle, there is usually an accelerated rise in the price of BTC, followed by a «shaking» correction.
From the moment the bottom forms at the end of the previous bearish trend, this peak remains the highest price point within the cycle until the halving itself.
However, it does not overlap the historical maximum established in the previous halving cycle.
This local peak is historically formed at a level of -33% (before the second halving) to -51% (before the first halving)
in relation to the maximum of the previous halving cycle.
Bitcoin price forms new all-time high after many monthsafterthe halving itself.
Brief results of a detailed analysis
- Most of the exponential rise in Bitcoin price associated with the halving occurred duringafterhalving
- The price of bitcoin updated the historical maximum after each halving.
- If the rally before halving was smaller, then the rally after the rally halving turned out to be larger and lasted longer than in the previous cycle.
- Before each halving there was a significant correction.
- The local peak before correction in the middle of the halving cycle has historically been the highest price point before halving, but not high enough to update the historical maximum.
How can a third halving affect the price of bitcoin?
We found quite a few trends in Bitcoin price changes as a result of halvings.
Now the question is whether we can use this information to determine what effect the upcoming third halving may have on the price of BTC.
People often tend to use historical market data to detect trends and patterns, and then extrapolate these data to potential future trends.
Although historical price changes may be useful in predicting future trends, never future price fluctuations will fully reproduce historical data.
Based on trends historically observed before and after halving, one can only guess how the price of bitcoin can behave in connection with the upcoming third halving.
With this caveat, let's look at the most important trends through the prism of historical price data and in the context of the future behavior of Bitcoin prices ahead of the third halving.
Predicting the effect of halving on the price of bitcoin using data from previous bitcoin halving cycles
1. In each of the halving cycles to this day, the price of bitcoin has grown by 12000–13000%
The first halving led to an increase in BTC prices by 13,378%, the second provoked a rally by 12,160%.
An increase of 12,160% of the December 2018 low ($ 3,150) yields a price of ~ $ 385,000 / BTC.
Similarly, a rally of 13,378% would give a price of ~ $ 425,000 / BTC.
The price of $ 385,000 per BTC opens up very interesting prospects, because this means that Bitcoin will surpass gold in market capitalization.
This, of course, could greatly enhance Bitcoin's status as "digital gold".
2. The local peak of the first part of the halving cycle, as a rule, is formed immediately before the halving, but it does not exceed the historical maximum established in the previous cycle
From mid-December 2018 to June 2019, bitcoin grew by more than 340%, which is pretty close to a 383 percent rally before Bitcoin’s second halving.
If bitcoin had grown by 383% this time, then the local peak would have been formed at the level of ~ $ 15,000 (instead of $ 13,900).
Such a course of events corresponds to the historical tendency of formation in anticipation of the halving of a new local peak, but not a historical maximum.
This would satisfy another important trend: with a smaller scale of the rally before the halving, the rally after the halving was stronger and lasted longer.
If this trend turns out to be fair this time too, then Bitcoin is more likely to expect growth of 13,000%, rather than 12,000%, as in the second halving cycle.
On the other hand, assuming that, likethe first halving cycle, bitcoin will undergo a growth of 663% even before the first halving, this will mean that it will reach almost $ 24,000 before the third halving.
Of course, this would lead to an update of the historical maximum to the moment of halving, which contradicts the trend observed in the past.
For this reason, the behavior of the price of Bitcoin can continue to closely follow the price fluctuations observed before the second halving.
If so, then Bitcoin will need more time to rally after halving (after all, in the second halving cycle, an increase of 12,000% and the establishment of a new historical maximum took more than 500 days).
If the price rally after the third halving will bereminiscent of a similar rally of the second halving cycle, then Bitcoin can fix a new historical maximum more than 500 days after the halving, i.e. around the 4th quarter of 2021.
3. The formation of a local peak and the subsequent correction will occur before halving
Correction is likely to happen even before the halving, and this will be an excellent financial opportunity for both traders and investors.
4. Bitcoin will update its historical price maximumafterhalving
Historically, Bitcoin has updated historical price highs after every halving.
Regardless of what price levels the peak of the current halving cycle will fall, most likely it will be formed many months after the halving.
Conclusion
The number of new bitcoins created every 10 minutes is halved every four years.
That's why halving is considered an important catalyst, stimulating a significant increase in the price of bitcoin.
Limiting the volume and pace of Bitcoin emissions ensures its scarcity.
And the exponential rise in the price of Bitcoin is a clear illustration of the most important principle of financial markets:scarcity increases cost.
It is important to understand and soberly evaluate the historical significance of the effect of halving on the price of bitcoin.
After all, historical price databitcoin show that halvings are a unique type of event that tend to make investors money, not just in the lead-up to the halving, but for many monthsafterhim.
Bitcoin halvings combine the simplicity of a narrative with a high probability of making a profit.
Of course, past results cannot guarantee future results.
But two things about history can be said with certainty:
- History does not lie.
And the words of Mark Twain:
- «History does not repeat itself, but it often rhymes».
</p>