Article Reading Time:
7 min.

Opinion
Default, recession and economiccrises are not the only global financial shocks that humanity faces. There is such a thing as stagflation, which is reflected in the crypto market.
What is stagflation
Stagflation is usually understood as a situation ineconomy when there is a simultaneous increase in inflation and unemployment. At the same time, the economy itself is in conditions of stagnation, that is, stagnation, or even in decline (hence the name “stagflation” - a derivative of “stagnation” and “inflation”).
Usually developing economiesThey are faced only with rising inflation, caused largely by the nature of fiat (state, paper) money, the monopoly of central banks on the issue and, in fact, the high rates of this issue. Stagflation is a phenomenon in which the actions of central banks are similar to those of high inflation, but in addition the economy itself does not grow fast enough. What could this lead to?
Consequences of stagflation
In stagflation, people face the followingproblem - personal financial planning is extremely difficult, they do not know what share of savings can be spent in the future. Inflation makes it difficult to plan and invest in the present because no one knows what the income will be after a certain time. In addition, unemployment is rising, causing even more uncertainty and even slower growth. In some cases, stagflation can even develop into a serious, protracted economic crisis.
But how does all this affect the crypto market?
Implications for the cryptocurrency industry
The cryptocurrency phenomenon exists, from the point of viewfrom the perspective of history, for a short time. Consequently, there is not enough data today on whether cryptocurrency is a good defensive investment during stagflation and whether the period of stagflation as a whole is clearly “good” or “bad” for the industry. To understand whether it is worth buying cryptocurrency during a period of stagflation, you can study how “traditional markets” behave during inflation or stagflation.
Stagflation (and recession with economiccrisis), naturally, is harmful to any traditional markets, and cryptocurrency markets have a high correlation with well-known indices. There is a metric that reflects the correlation between the BTC rate and the S&P 500 index (for example, from early March to mid-May 2023, their correlation
was positive).
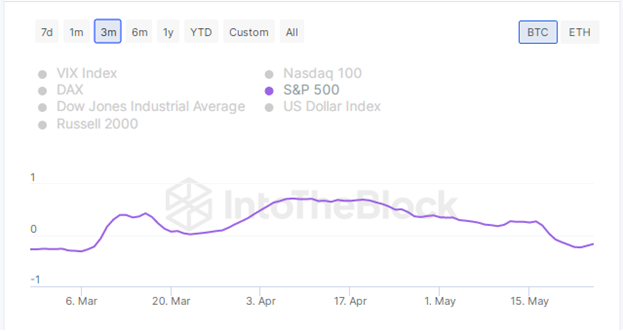
Source: app.intotheblock.com
Note:The correlation coefficient value ranges from -1 to 1.
This means that negative moods cantrickle down from traditional financial assets into cryptocurrencies. Moreover, the days when cryptocurrency was the object of interest of individual enthusiasts, rather than large hedge funds, are long gone. Large institutional investors are now pursuing a strategy of risk diversification with digital assets as part of their portfolio.
Usually in financial conditionsDue to uncertainty, investors prefer easily predictable instruments with low volatility. The goal: not so much to increase capital as to preserve savings. Cryptocurrency is highly volatile, so demand for it (especially for extremely volatile altcoins like modern meme coins) may be less than usual. Stagflation harms cryptocurrency markets and the industry as a whole by reducing the interest of retail investors in purchasing electronic decentralized money. High inflation directly affects the amount of free money in people’s hands, including for the purchase of cryptocurrency. Let us also recall the growth of unemployment, when the investment planning horizon is significantly reduced for a banal reason: if a person loses his job, he should have savings on hand that will allow him to “stay afloat” for some time. In this sense, prolonged periods of correction (also known as “crypto winters”) are clearly against the interests of the investor.
Pros of cryptocurrency
However, individual financiers and playersThe crypto industry prefers investments in cryptocurrency specifically during periods of economic instability against the backdrop of a protracted correction. As an example, we can cite individual mining companies that are increasing their positions during the crypto winter and their investors/creditors who are in no hurry to demand back the invested funds, counting on high income in the future.
Selecting investments in similar assetsinstead of traditional financial instruments, this is also due to the fact that cryptocurrencies operate on the blockchain and are not tied to the monetary policy of a specific country. When inflation rises in that particular country, investors can still benefit from the profits generated by the investment into cryptocurrency. Even if their national currency loses value due to inflationary pressures.
Investors often look for a way to protectsavings from stagflation. This is especially true for countries such as Venezuela or Argentina, where hyperinflation is often observed - a rapid and uncontrollable increase in prices for vital goods and services. Here, investing in cryptocurrency works well during periods of economic instability, as it represents an alternative means of payment. And despite their volatility, they turn out to be more stable and predictable, in comparison with rapidly depreciating banknotes. Residents of such regions can try to find a solution to their problems by redirecting part of their reserves to BTC.
Crisis and Bitcoin
Since stagflation is accompanied by highinflation and economic downturn, BTC can, with some reservations, be considered as a means of protecting against inflation and at the same time as a risky (volatile) asset, the price of which can also fall during an economic downturn.
BTC in this sense is often compared to gold,which has traditionally served as a hedge against inflation. Why does the first cryptocurrency even claim to be an insurance against inflation? First, Bitcoin is a decentralized global means of payment, not under the control of central authorities. Governments do not have direct control over issuance and transactions, which makes Bitcoin less susceptible to monetary policy. In addition, BTC is a scarce asset, as no more than twenty-one million of these digital coins can go into circulation. BTC is sometimes called a “deflationary currency” because the maximum emission is limited programmatically and the rate of influx of new coins into the economy tends to decrease due to halving.
More than 92% of the total coins have already been mined.
Because of this scarcity, Bitcoin is also called"digital gold" Typically, prices for risky investments fall when interest rates rise. Since the cryptocurrency market has developed a significant correlation with the stock market, much will depend on whether BTC can break its correlation. This process will likely take longer given the widespread adoption of the asset.
Stagflation (or serious crisis)hypothetically could become a catalyst for the public acceptance of BTC and other cryptocurrencies, some experts believe. Among them is Bloomberg senior commodities analyst Mike McGlone, who believes that in the future Bitcoin will be a “conditionally risk-free asset” amid the problems of traditional financial institutions. And former MicroStrategy CEO Michael Saylor is convinced that BTC has already “outperformed all assets in the stock market.”
This could happen if it turns out thatA “debt economy” is unviable in the long term. The tipping point could come when public trust in BTC exceeds trust in the modern economic system. It is worth noting that the first cryptocurrency arose at approximately the same time as the mortgage crisis in the United States (which turned into a global financial crisis) and could not become a mass “protective instrument” for objective reasons. On the other hand, in recent years there have not been many significant global economic crises in the world (except for the consequences of the pandemic), and BTC is only increasing its turnover, capitalization and popularity. This likely explains the gradual nature of Bitcoin's adoption as a defensive tool.
This material and the information in it does not constitute individual or other investment advice. The opinion of the editors may not coincide with the opinions of the author, analytical portals and experts.




